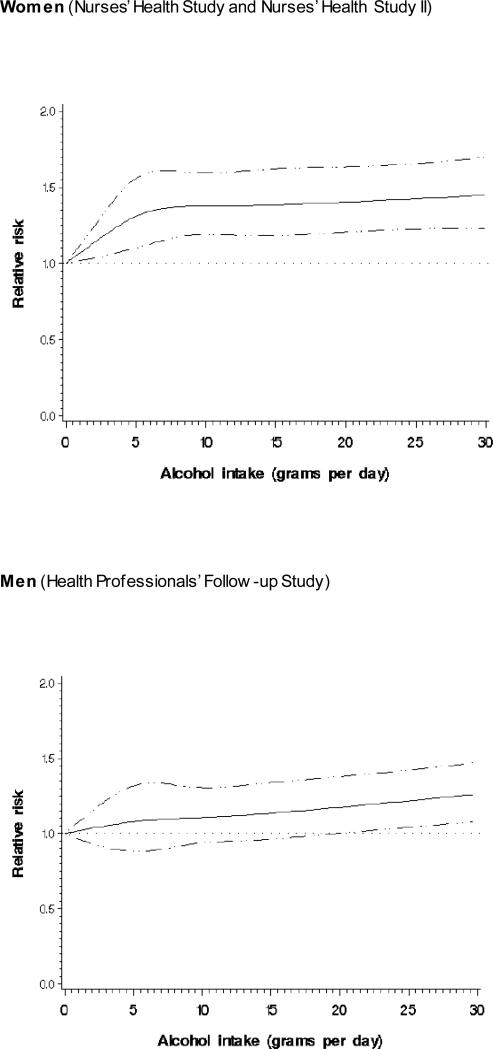
Fig 1.
Dose-response relative risk (solid line) and 95% confidence interval (dotted lines) of invasive cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma by alcohol intake (grams per day) for women and men. Model was adjusted for age, BMI, smoking status and pack-years smoked, physical activity, caffeine intake, family history of melanoma, tanning ability, lifetime number of severe sunburns, number of moles, natural hair colour, and average annual UV-B flux at place of residence.