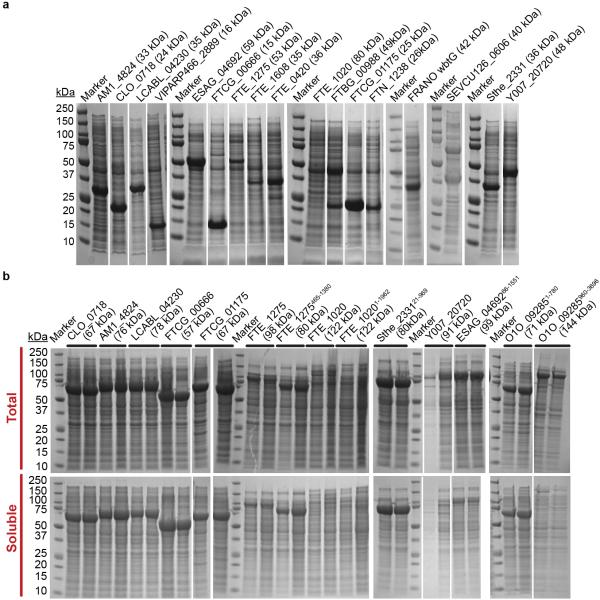
Extended Data Figure 7. In vivo expression of synthetic genes with sequences optimized using the 31C-FO method.
a, Coomassie-blue-stained SDS–PAGE gels of whole-cell extracts after overnight induction at 18 °C of synthetic genes designed using the 31C-FOH method for 17 different proteins. All genes were cloned in-frame with a C-terminal hexa-histidine tag in the same pET21 plasmid derivative used to generate our large-scale protein-expression data set38. Equal volumes of induced cultures were loaded in all lanes. b, Coomassie-blue-stained SDS–PAGE gels of whole-cell extracts (top) and the corresponding soluble fractions (bottom) after overnight induction at 18 °C of 14 of the same synthetic genes fused in-frame at the C terminus of the gene for the E. coli maltose-binding protein (MBP). The protein sequences come from the following source organisms: LCABL_04230 from Lactobacillus casei BL23; VIPARP466_2889 from Vibrio parahaemolyticus; AM1_4824 from Acaryochloris marina MBIC11017; CLO_0718 from Clostridium botulinum E1; ESAG_04692 from Escherichia sp. 3_2_53FAA; FTCG_00666 and FTCG_01175 from Francisella tularensis subsp. novicida GA99-3549; FTE_1275, FTE_1608, FTE_0420 and FTE_1020 from Francisella tularensis subsp. novicida FTE; FRANO wbtG and A1DS62_FRANO from Francisella novicidal; FTBG_00988 and A7JEH2_FRATL from Francisella tularensis subsp. tularensis FSC033; FTN_1238 from Francisella tularensis subsp. novicida U112; O1O_09285 from Pseudomonas aeruginosa MPAO1/P1; Sthe_2331 from Sphaerobacter thermophilus DSM20745/S6022; SEVCU126_0606 from Staphylococcus epidermidis VCU126; and Y007_20720 from Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Montevideo 507440-20.