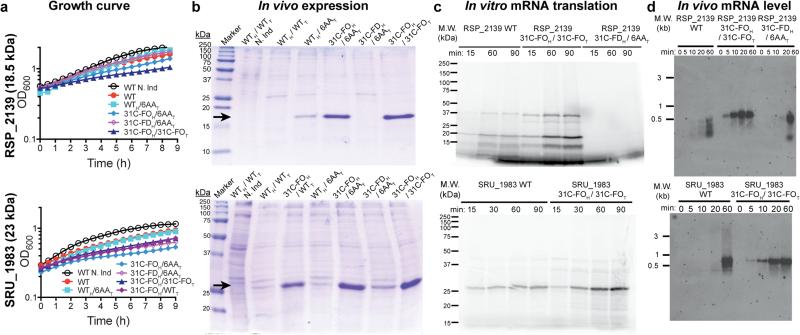
Figure 5. Analyses of synthetic genes designed to enhance protein expression.
Synonymous variants of inefficiently translated native (WT) genes were redesigned in the head or tail or both using the 6AA, 31C folding optimized (31C-FO), or 31C folding deoptimized (31C-FD) methods. The type of sequence in the head (subscript H) and tail (subscript T) is indicated separately. “N. Ind.” indicates non-induced control. (a) Growth curves at room temperature after induction at time zero in E. coli BL21(DE3). (b) Coomasie Blue stained SDS-PAGE gels of cells induced overnight at 18° C, with loads normalized to final OD600. Black arrows indicate the target proteins. (c) Autoradiographs of SDS-PAGE gels of in vitro translation reactions in the presence of [35S]-methionine using fully purified components to translate an equal amount of purified mRNA transcribed in vitro by T7 RNA polymerase. Higher molecular weight bands represent SDS-resistant oligomers. (d) Northern blots of equal amounts of total RNA isolated at the indicated times after induction, hybridized with a probe matching the 5’UTR.