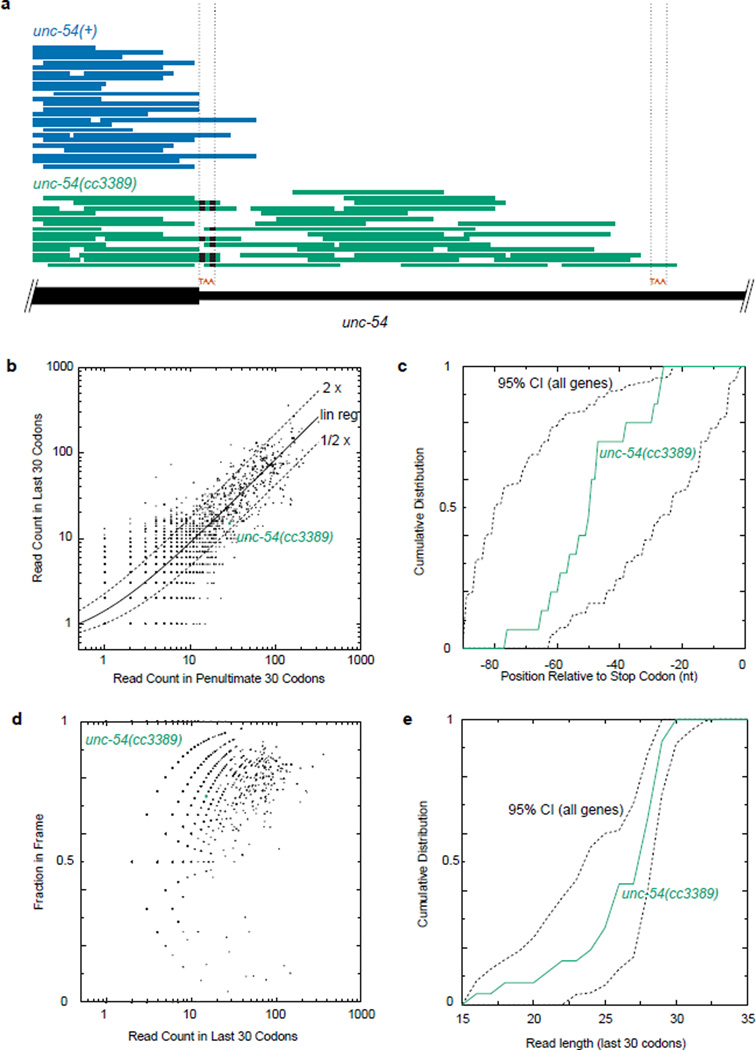
Extended Data 7. Ribo-seq of unc-54(cc3389) shows an unexceptional progression of ribosomes in the readthrough region.
a. Raw Ribo-seq reads for unc-54(+) (blue) and unc-54(cc3389) (green) animals, plotted as read pile-ups. Mismatched bases are indicated with black bars. Location of the normal stop codon and the first in-frame stop codon are indicated with “TAA” and dotted lines. The extension in unc-54(cc3389) is 30 amino acids.
b. Number of Ribo-seq reads in the last 30 codons, compared to the previous 30 codons, for all mRNAs. Linear regression was performed on all points (solid line), and two-fold difference shown (dashed lines).
c. The distribution of Ribo-seq reads in the last 30 codons (90nts) of unc-54(cc3389) is shown in green, and the 95% confidence interval for all open reading frames in dashed lines.
d. The fraction of in-frame Ribo-seq reads in the last 30 codons is plotted as a function of read counts in the last 30 codons, and unc-54(cc3389) highlighted.
e. The distribution of read lengths in the last 30 codons of unc-54(cc3389), and all open reading frames (95% confidence interval, dashed lines).
For b–d, reads were restricted to 28,29,30 nt lengths. For b–e, a 12 nt offset was done for the ribosomal P-site, and read counts were derived solely from the unc-54(cc3389) Ribo-seq library. For c and e, a minimum 15 read counts was imposed to obtain the 95% CI from "all genes".