Figure 1.
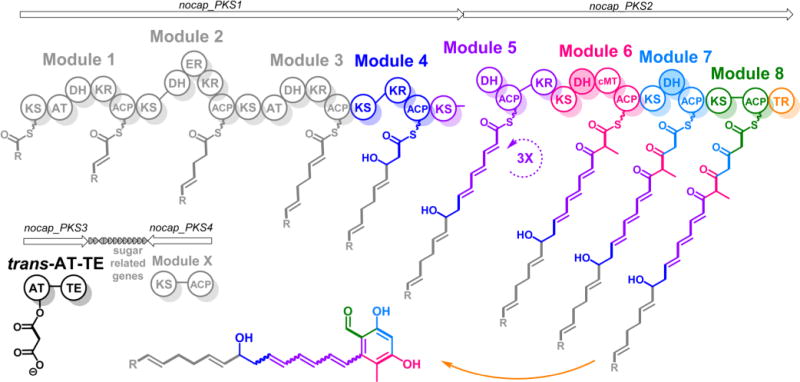
NOCAP synthase is comprised of eight PKS modules distributed across two large proteins. A third didomain protein has a trans-acyltransferase (AT) and thioesterase (TE). NOCAP_PKS1 has four modules and the ketosynthase (KS) of a fifth. NOCAP_PKS2 includes the dehydratase (DH), ketoreductase (KR), and acyl carrier protein (ACP) domains of module 5 along with three more trans-AT modules. The KR domain of module 5 is atypically located C-terminal to its ACP domain. Module 6 has a C-methyltransferase (cMT). The putative (shaded) DH domains of modules 6 and 7 are likely vestigial, as dehydratase active site residues were not observed. Chain release is by an NAD(P)H-dependent thioester reductase (TR). The proposed biosynthetic scheme is based on observed polyketide products of modules 4–8 (highlighted in color). Because the activity of modules 1–3 was not reconstituted in this study, the predicted structure of the tetraketide intermediate (shown in gray) is tentative. The R-group indicates that the primer unit of module 1 is unknown. All modules besides modules 1 and 3 require the trans-AT to supply malonyl extender units. The function of module X (NOCAP_PKS4) is also unknown.
