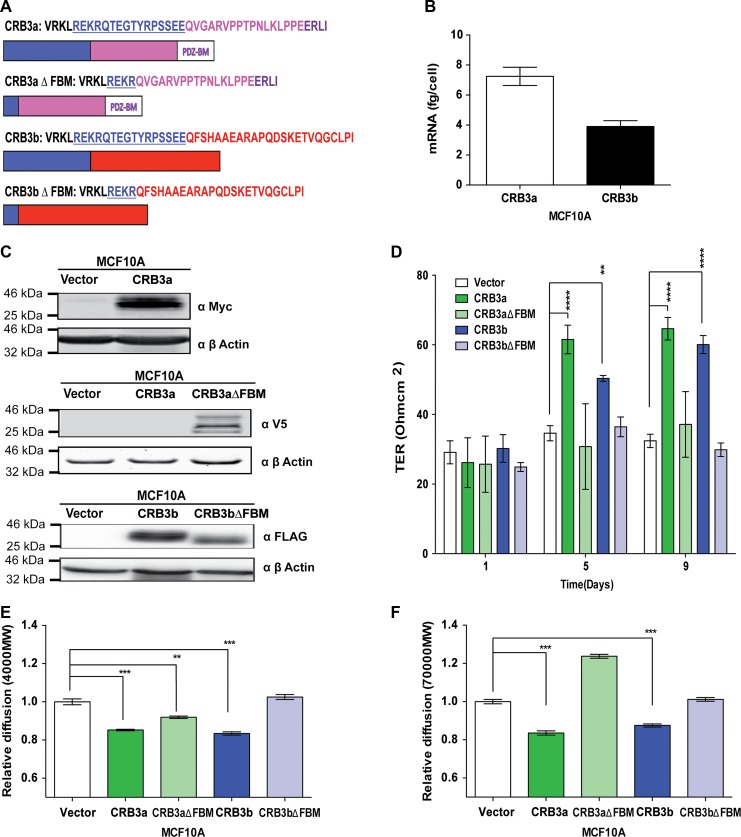
Figure 1.
CRB3b induces mature TJs in MCF10A cells. (A) Schematic diagram of the different CRB3 intracellular domains and deletion mutants used in this study: CRB3a with the FBM, C-terminal, and the PDZ-binding region; CRB3b with the FBM and the differing C-terminal. FBM deletion mutants of the CRB3 isoforms were engineered to disrupt CRB3−FERM protein interactions. (B) Absolute qRT-PCR analysis of the two isoforms of CRB3 in MCF10A cells shows higher levels of CRB3a mRNA than CRB3b. Error bars represent ±SD (n = 9). (C) Immunoblots show MCF10A-Vector, MCF10A-CRB3a, and MCF10A-CRB3aΔFBM cells probed with either MYC or V5 antibody or MCF10A-Vector, MCF10A-CRB3b, and MCF10A-CRB3bΔFBM cells probed with FLAG antibody for presence of ectopic proteins. β-actin was used as a loading control. (D) MCF10A-Vector, MCF10A-CRB3a, MCF10A-CRB3aΔFBM, MCF10A-CRB3b, and MCF10A-CRB3bΔFBM cells were grown on 0.4-μm PET membranes, and TER was recorded. Error bars represent ±SD (n = 9). (E and F) Size-selective assessment of TJ paracellular flux on MCF10A-Vector, MCF10A-CRB3a, MCF10A-CRB3aΔFBM, MCF10A-CRB3b, and MCF10A-CRB3bΔFBM cells using fluorescently labelled dextrans. Cells were grown for 5 days on 0.4-μm PET membranes prior to addition of fluorescent 4-kDa dextran–FITC (E) and 70-kDa dextran–Rhodamine (F). Error bars represent ±SD (n = 9). For all experiments, a two-way ANOVA was used with Bonferroni correction to compare against MCF10A-Vector. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.