Figure 5.
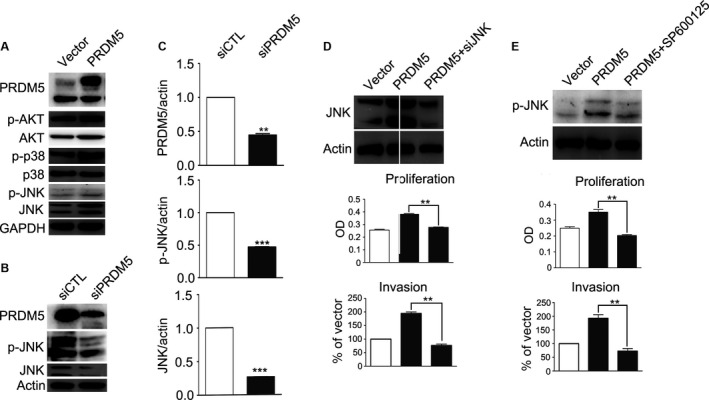
JNK pathway is involved in PRDM5‐mediated proliferation of murine melanoma cells. (A) Western blot showed that the expression of JNK and phosphorylated JNK was elevated in cells transfected with pXJ‐40‐PRDM5. GAPDH was used as a loading control. (B) The expression of JNK and phosphorylated JNK was inhibited in cells transfected with PRDM5 siRNA. Actin was used as a loading control. (C) Levels of PRDM5, p‐JNK, and JNK were quantified by densitometry and normalized to actin. (D) Western blot shows that PRDM5‐induced JNK expression was inhibited by JNK siRNA. Actin was used as a loading control. MTT assay and transwell invasion assay were performed to determine the proliferation and invasiveness of cells cotransfected with pXJ‐40‐PRDM5 and JNK siRNA. (E) Cells were incubated with SP600125 for 1 h, and total protein was extracted for western blot with antibodies against phosphorylated JNK or actin. MTT assay and transwell invasion assay were performed to determine the proliferation and motility of cells transfected with pXJ‐40‐PRDM5 after SP600125 treatment. *P<0.05, versus control group. **P<0.01 versus control group. ***P<0.001 versus control group. MTT, 3‐[4, 5‐dimethylthiazol‐2‐yl]‐2, 5‐diphenyltetrazoliumbromide.
