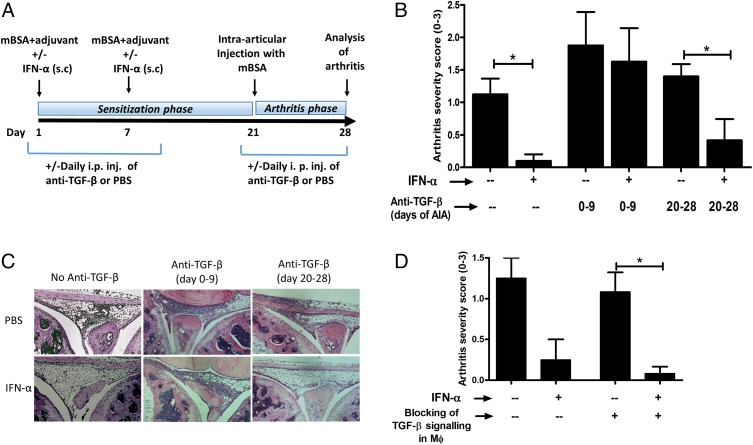
FIGURE 1.
The protective effect of IFN-α against AIA is mediated by TGF-β signaling in the sensitization phase. (A) Schematic representation of the AIA model, as described in Materials and Methods. Briefly, AIA was induced in WT Sv129 mice and LysM Cre+/−Tgfbr2fl/fl with or without IFN-α treatment. TGF-β signaling was blocked in WT mice by daily i.p. injection of 150 μg anti–TGF-β Ab for the first 0–8 or 20–28 d of AIA. (B) The level of arthritis is expressed as severity score (mean ± SEM, n ≥ 4) from WT mice with or without IFN-α and anti–TGF-β treatment. (C) Representative histochemical slides showing inflammation of the knee joint from each group. (D) Level of arthritis expressed as severity score (mean ± SEM, n ≥ 6) from LysM Cre+/−Tgfbr2fl/fl mice with or without IFN-α treatment. Comparison of arthritis severity score between different treatment groups was done by Mann–Whitney U test (*p < 0.05).