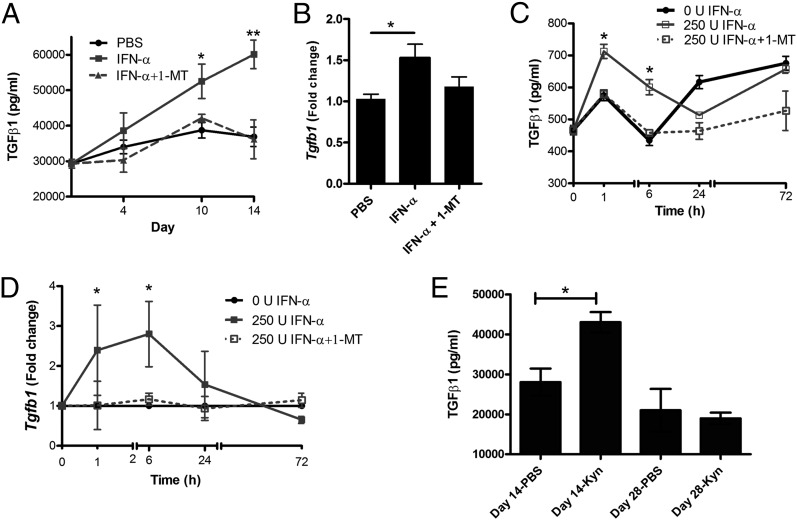
FIGURE 6.
The enzymatic activity of IDO1 regulates IFN-α–induced TGF-β production in vivo and in vitro. (A and B) Female mice were immunized days 1 and 7 with mBSA with or without IFN-α treatment, with or without 1-MT administered in drinking water, as described for AIA in Materials and Methods. Levels of TGF-β in serum were determined by ELISA at the indicated time points after the first immunization (A), and TGF-β mRNA levels in spleens were determined by RT-PCR at day 10 (B). For in vitro studies, splenocytes isolated day 10 from mBSA-sensitized mice were restimulated ex vivo with 50 μg/ml mBSA with or without 250 U IFN-α, with or without 5 μM 1-MT. Depicted in (C) are the levels of TGF-β in culture supernatants determined by ELISA, and in (D) the TGF-β mRNA levels in cultures cells as determined by RT-PCR at the indicated time points. In (D), data are expressed as fold change normalized to reference gene Actb and Tgfβ expression in mBSA-stimulated cultured cells from the same mice. Comparison of TGF-β levels between groups in vivo (A, n = 8; B, n < 5) was done by the Mann–Whitney U test and in vitro (C and D, n = 5) by Student t test for paired observations (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01). (E) Female mice were immunized days 1 and 7 with mBSA with or without Kyn treatment, and the levels of TGF-β in serum were determined by ELISA at day 14 (n = 4–6) and day 28 (n = 3) after the first immunization. Comparison between groups was made by Mann–Whitney U test.