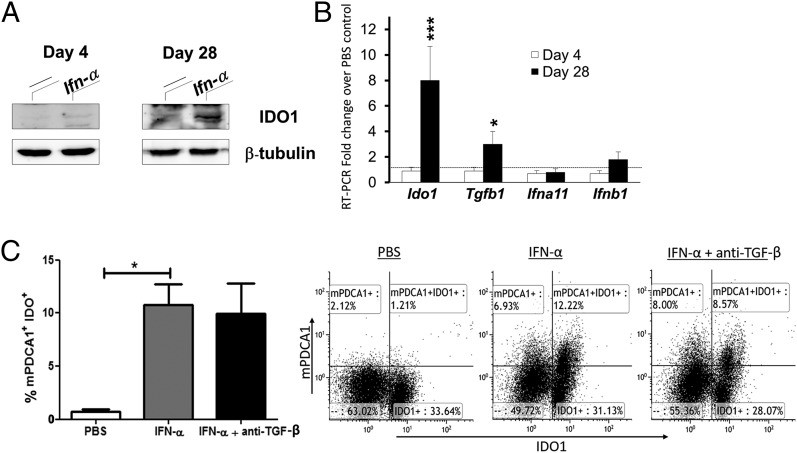
FIGURE 8.
IFN-α induces IDO1 expression in splenic pDC in vitro and in vivo independently of TGF-β. AIA was induced in female mice with IFN-α treatment, as described in Materials and Methods. At days 4 and 28, mice were sacrificed and pDC were purified from their spleens. (A) Western blot analysis of IDO1 protein expression in pDC. (B) Real-time PCR analysis of Ido1, Tgfb1, Ifna11, and Ifnb1 transcripts in pDC isolated from spleen cells at days 4 and 28 of AIA from mice treated with IFN-α, normalized to the expression of Actb, and presented relative to results of pDC isolated from control mice not treated with IFN-α (dotted line, 1-fold). (C) Splenocytes were isolated at day 10 of AIA, stimulated with 50 μ/ml mBSA plus 250 U/ml IFN-α, with or without anti–TGF-β (40 μg/ml) for 72 h, and analyzed for IDO1-positive pDC by FACS (see Materials and Methods). The bar diagram (left) depicts the percentage of mPDCA+IDO1+ cells among the live lymphocyte population, and the FACS plots (right) show representative dot plots from one of five mice. Data in (A) are the representative of four experiments, and (B) and (C) (mean ± SD, n = 6) were analyzed by Student t test. *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001.