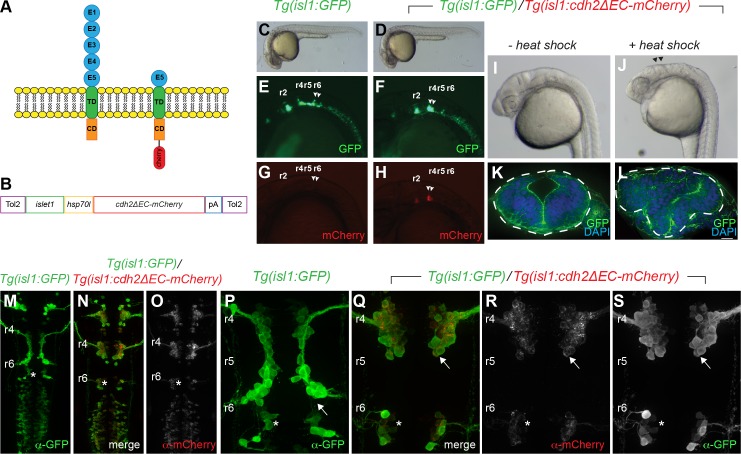
Fig 1. Generation of stable transgenic fish expressing dominant-negative Cadherin-2 in cranial branchiomotor neurons.
(A) Schematic representation of full length Cadherin-2 (N-cadherin) and extracellular domain-deleted Cadherin-2 (Cdh2ΔEC) fused with mCherry that functions as a dominant-negative protein. E1-E5 cadherin ectodomains; TD, transmembrane domain; CD, cytoplasmic domain. (B). Schematic representation of plasmid used to generate stable transgenic fish expressing cdh2ΔEC-mCherry driven by the zCrest1 enhancer element of the islet1 promoter (islet1) upstream of the minimal promoter (hsp70l). (C,D) Photographs of wild-type Tg(isl1:GFP) and Tg(isl1:GFP)/Tg(isl1:cdh2ΔEC-mCherry)vc25 embryos at 24hpf, showing normal morphology. (E-H) Lateral images at 24 hpf of the green and red channels showing GFP-expressing and Cdh2ΔEC-mCherry-expressing cranial branchiomotor neurons in Tg(isl1:GFP) fish and Tg(isl1:cdh2ΔEC-mCherry) transgenic fish. Arrowheads point to FBMNs. (I,J) Lateral images of Tg(isl1:GFP)/Tg(isl1:cdh2ΔEC-mCherry)vc25 embryos at 24hpf with and without heat shock. Arrowheads denote defects at midbrain-hindbrain region after heat shock. (K,L) Cross sections through hindbrain neuroepithelium of Tg(isl1:GFP)/Tg(isl1:cdh2ΔEC-mCherry)vc25 embryos before and after heat shock labeled with DAPI and Alexa-488-phalliodin. Dotted lines outline the neural tube. (M-S) Confocal micrographs of immunostained embryos showing low-magnification (M-O) and high magnification (P-S) dorsal views of wild-type Tg(isl1:GFP) (M,P) and Tg(isl1:GFP)/Tg(isl1:cdh2ΔEC-mCherry)vc25 embryos (N,O,Q-S) at 26 hpf. Embryos were labeled with α-GFP and α-mCherry showing that Cdh2ΔEC-mCherry is only expressed in cranial branchiomotor neurons and not the surrounding neuroepithelium. Arrow points to the abnormal position of FBMNs in Tg(isl1:cdh2ΔEC-mCherry)vc25 embryos. Rhomobomeres (r2-r6) are indicated. White asterisk denotes r6-derived PLL efferent neurons, which differ from r4-derived FBMN populations.