Figure 1. Construction of ΔflbB mutant and determination of polar effect on downstream genes expression.
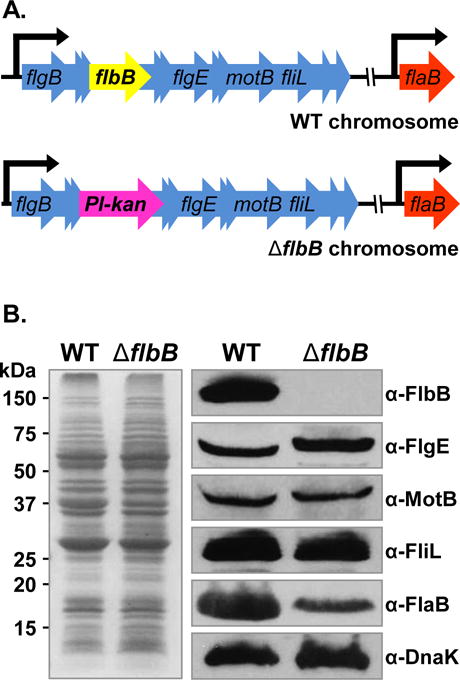
(A) Schematic diagrams of wild-type and ΔflbB mutant genomes. flaB gene (bb0147) is separated from the targeted flbB gene (bb0286) by approximately 100 kb. WT B. burgdorferi with the flgB polycistronic operon containing the targeted flbB is shown in top panel. The Pl-kan cassette replacing the flbB gene by allelic exchange is shown in bottom panel. The model lists only a few of the 26 genes of the flgB operon, and other genes are indicated by multiple arrowheads. (B) Confirmation of flbB gene-deletion and determination of polar effect by western blotting. WT and ΔflbB mutant cell lysates were subjected to SDS-PAGE (left) followed by immunoblotting (right). Immunoblotting was performed with B. burgdorferi FlbB, FlgE, MotB, FliL, or FlaB-specific antibodies. DnaK was used as a loading control. FlbB antiserum reacted with a 14 kDa protein in the wild-type lysate that is absent in the ΔflbB lysates indicate that this protein is the FlbB (FlbB blot).
