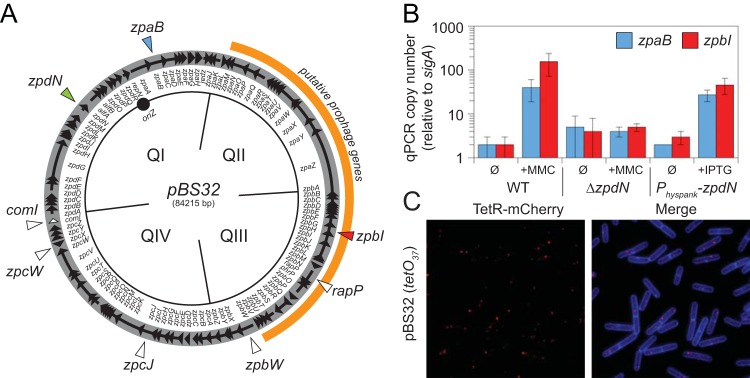
FIG 1.
pBS32 copy number increases in response to mitomycin C treatment. (A) Map of the pBS32 plasmid (open circle) divided into conceptual quadrants (QI, QII, QIII, and QIV). Arrows indicate open reading frames, and internal annotations indicate the identity of the adjacent genes. Origin (oriZ) is indicated by a solid circle. The region of putative prophage genes is outlined in orange. Genes mentioned in the text are indicated by triangles. (B) Plasmid copy number as determined by quantitative PCR (qPCR). WT strain 3610 and a ΔzpdN mutant (DK3287) at an OD600 of 0.1 were grown for 90 min in the presence (+MMC) or absence (Ø) of 0.3 μg/ml mitomycin C prior to being harvested for DNA isolation. A strain containing a Physpank-zpdN construct (DK1634) at an OD600 of 0.1 was grown for 60 min in the presence (+IPTG) or absence (Ø) of 1 mM IPTG prior to being harvested for DNA isolation. qPCR was performed on the isolated DNA using primer pairs specific for two different plasmid loci, zpaB and zpbI, and compared to qPCR performed using primer pairs specific for a chromosomal locus, sigA. Plasmid copy number was calculated as described previously (13). (C) Fluorescence microscopy in which TetR-mCherry foci (false colored red) and membrane stained with TMA-DPH (false colored blue) are indicated for strain DK280, which encodes a constitutively expressed TetR-mCherry construct, and an array of 37 copies of the tetO operator sequence were integrated into pBS32.