Fig. 1.
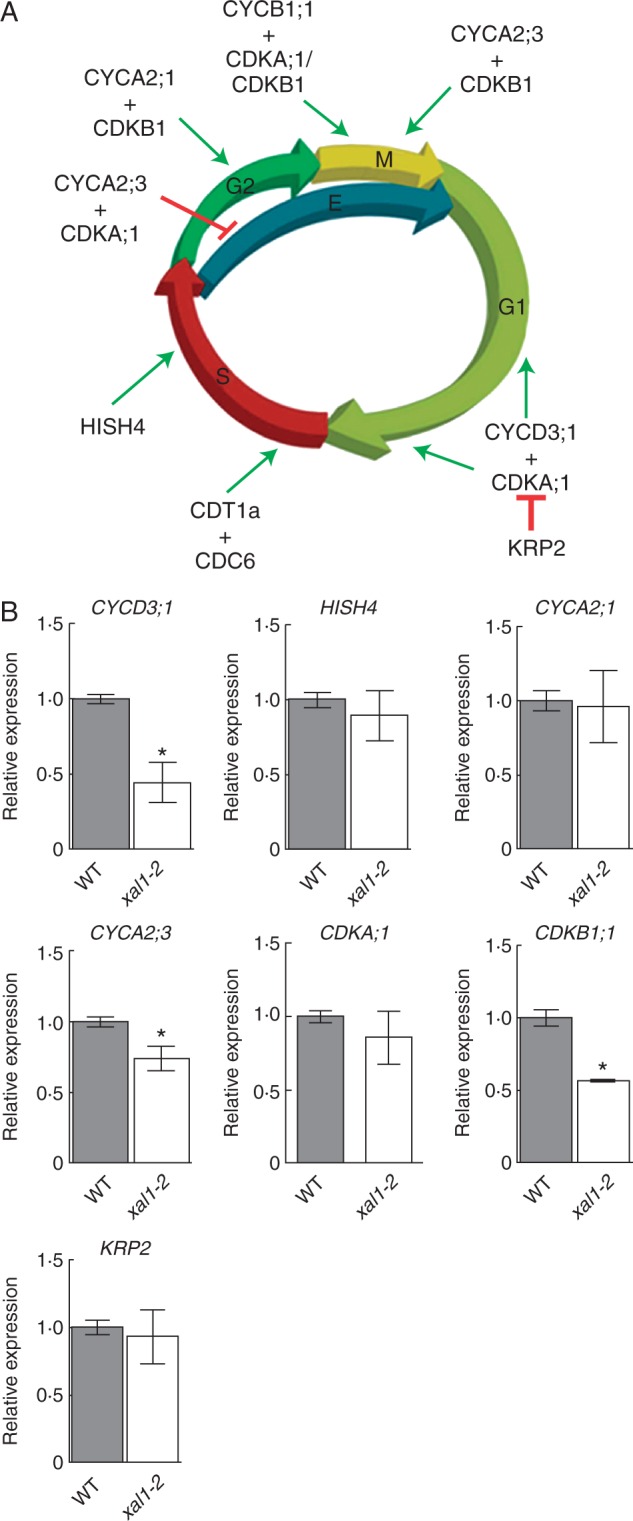
XAL1 is necessary for CYCD3;1, CYCA2;3 and CDKB1;1 transcriptional regulation. (A) Schematic representation of the participation of some genes in Arabidopsis cell-cycle transitions. The CYCD3;1/CDKA1 complex triggers G1–S phase by phosphorylation of RB-E2F pathway (not shown) and is essential for cell proliferation. This complex could be inhibited by KRP2 depending on hormonal conditions. CDT1a and CDC6 form the pre-replication complex performing in S phase. During G2 phase, cyclins CYCA2;3, CYCB1;1 and CYCB1;4 are associated with other CDK types (A or B), promoting transition to G2–M and their regulation is important for repressing the endoreplicative cycle. (B) Relative expression levels of some cell-cycle components in xal1-2 compared with wild-type (WT) roots at 5 dpg, showing that CYCD3;1, CYCA2;3 and CDKB1;1 are down-regulated in the mutant. Relative expression data are expressed as the mean ± s.d. and statistically significant differences from WT (*P < 0·05) were obtained by the Kruskal–Wallis test.
