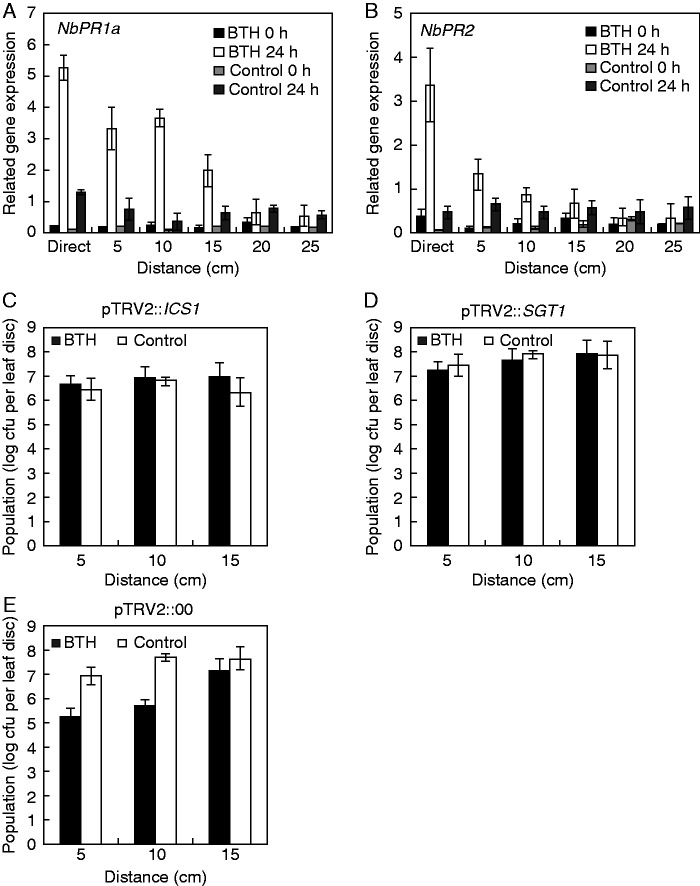
Fig. 3.
Transcriptional expression of defence genes and virus-induced gene silencing to validate salicylic acid (SA)-dependent signalling. The expression levels of SA-dependent resistance genes NbPR1 (A) and NbPR2 (B) were assessed by qRT–PCR. Bars represent the mean value ± s.e.m. (n = 4). The housekeeping gene NbActin was used as a control. The experiment was repeated twice with similar results. Effect of virus-induced gene silencing (VIGS) of NbICS1 (C) and NbSGT1 (D) on root-mediated transmission of systemic acquired resistance. Two-week-old N. benthamiana seedlings were infiltrated with Tobacco rattle virus 2-vector (TRV2) vector control (E) or TRV2 harbouring NbICS1 (C) and NbSGT1 (D), and monitored for 2 weeks. The silenced N. benthamiana plants were treated with BTH or water (control) for 7 d and inoculated with 108 cfu mL–1 R. solanacearum in plants pre-treated with BTH or water and their neighbouring plants. The experiment was repeated three times with similar results.