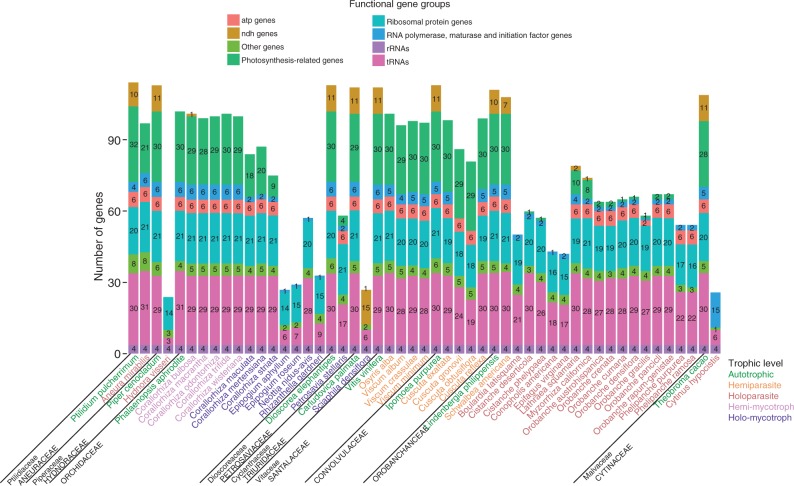
Fig. 1.
Number of unique plastid genes in each functional group of parasite and mycoheterotroph species and their closest autotrophic relative for which the whole plastome has been sequenced (Ptilidium: Forrest et al., 2011; Piper: Cai et al., 2006; Phalaenopsis: Chang et al., 2006; Dioscorea: Hansen et al., 2007; Carludovica: Lam et al., 2015; Vitis: Jansen et al., 2006; Ipomoea: McNeal et al., 2007; Lindenbergia: Wicke et al., 2013; Theobroma: Kane et al., 2012; all references concerning parasitic species are cited in the main text). The species are grouped by the family to which they belong (indicated in grey capital letters). The family of the autotrophic relative is indicated in lower-case letters when it belongs to a different family.