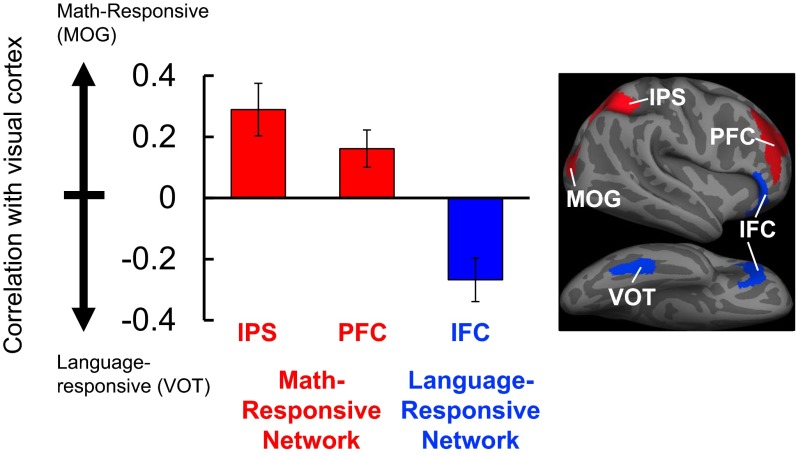
Fig. 3.
Resting-state correlations of visual and frontoparietal areas in the blind group (n = 13) are related to function. On the y axis is the difference between correlations across number- and language-responsive regions of visual cortex. Positive scores (red) indicate stronger correlation with number-responsive visual cortex (MOG), and negative scores (blue) indicate stronger correlation with language-responsive visual cortex (VOT) (error bars represent SEM). Number-responsive frontoparietal areas (IPS, PFC) are more correlated with number-responsive visual area (MOG), whereas language-responsive inferior frontal cortex (IFC) is more correlated with language-responsive visual area (VOT). See Fig. S7 for correlations in sighted group.