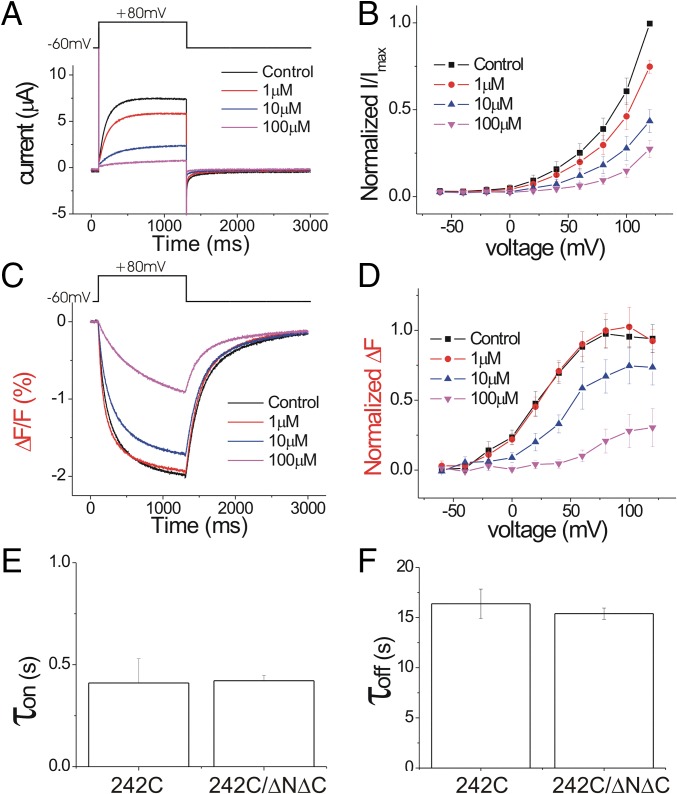
Fig. 6.
Zn2+ inhibits similarly monomeric and dimeric Hv1 channels. (A) Currents in response to a +80-mV voltage pulse in the presence of increasing extracellular Zn2+ concentrations on Alexa488-maleimide–labeled Hv1 ΔNΔC channels. (B) Normalized tail currents (Itail/Imax) versus voltage curves in the presence of increasing extracellular Zn2+ concentrations (n = 4). (C) Fluorescence changes (ΔF) in response to a +80-mV voltage pulse in the presence of increasing extracellular Zn2+ concentrations. (D) Normalized fluorescence changes (ΔFtail/ΔFmax) versus voltage curves in the presence of increasing extracellular Zn2+ concentrations (n = 4). (E and F) Time constants for (E) Zn2+ inhibition and (F) recovery from Zn2+ inhibition for dimeric S242C and monomeric S242/ΔNΔC channels.