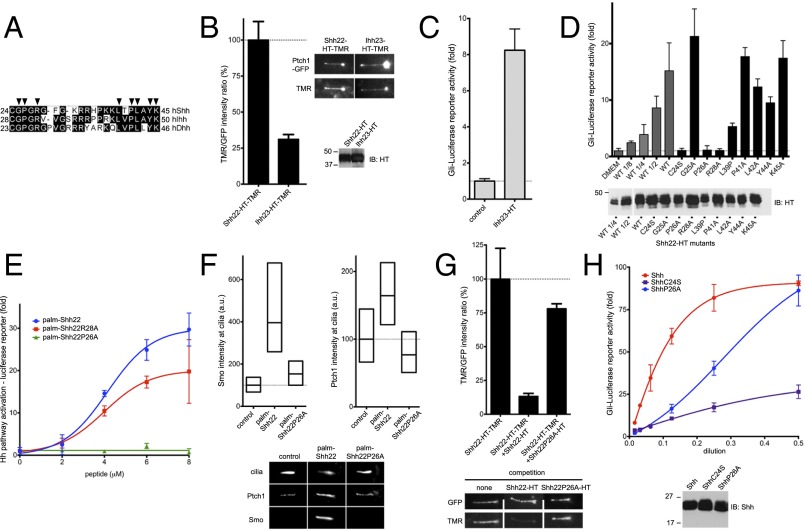
Fig. 4.
Holoprosencephaly-causing Shh mutation abolishes palmitate-dependent Ptch1 interaction. (A) Alignment of N termini of human Shh, Indian Hh (Ihh), and Desert Hh (Dhh). Arrowheads indicate residues that were tested by mutagenesis. (B) Binding of Shh22-HT-TMR and Ihh23-HT-TMR to cilia in Ptch1-null cells rescued with Ptch1-eGFP was measured by live imaging. Graph shows the ratio of ciliary TMR and GFP fluorescence. Error bars represent SE (n > 5 cilia). Representative images are shown on the right. Equal volumes of HT fusions were analyzed by SDS/PAGE and immunoblotting. Both fusions bind Ptch1. (C) Ihh23-HT activates Hh signaling in Shh Light II cells. Error bars represent SD (n = 3). (D) Wild-type and point mutants of Shh22-HT were expressed as secreted proteins in 293T cells, and their activity was assayed in Shh Light II cells as in C. A portion of 293T-conditioned media was analyzed by SDS/PAGE and immunoblotting to measure protein secretion. All fusions are active, except Shh22P26A-HT and Shh22R28A-HT. (E) Shh Light II cells were treated with palm-Shh22, palm-Shh22P26A, or palm-Shh22R28A, and Hh pathway activity was measured as in C. Palm-Shh22P26A is inactive, in contrast to palm-Shh22R28A. (F) Ptch1-null cells expressing Ptch1-eGFP were incubated with control media, palm-Shh22, or palm-Shh22P26A (5 μM each), and Smo and Ptch1 localization at cilia was measured by immunofluorescence and automated image analysis (n > 300 cilia). Representative cilia micrographs are shown under the graphs. Palm-Shh22P26A is defective in Smo and Ptch1 recruitment to cilia. (G) Ptch1-null cells expressing Ptch1-eGFP were incubated with Shh22-HT-TMR in the presence or the absence of excess Shh22-HT or Shh22P26A-HT. Binding of Shh22-HT-TMR to Ptch1-eGFP at cilia was measured as in B (n > 5 cilia). Shh22P26A-HT is defective in competing Shh22-HT-TMR binding to Ptch1-eGFP. (H) As in E, but cells were treated with Shh, ShhC24S, or ShhP26A. Equal volumes of each ligand were analyzed by SDS/PAGE and immunoblotting. ShhP26A is less active than Shh, but more active than ShhC24S.