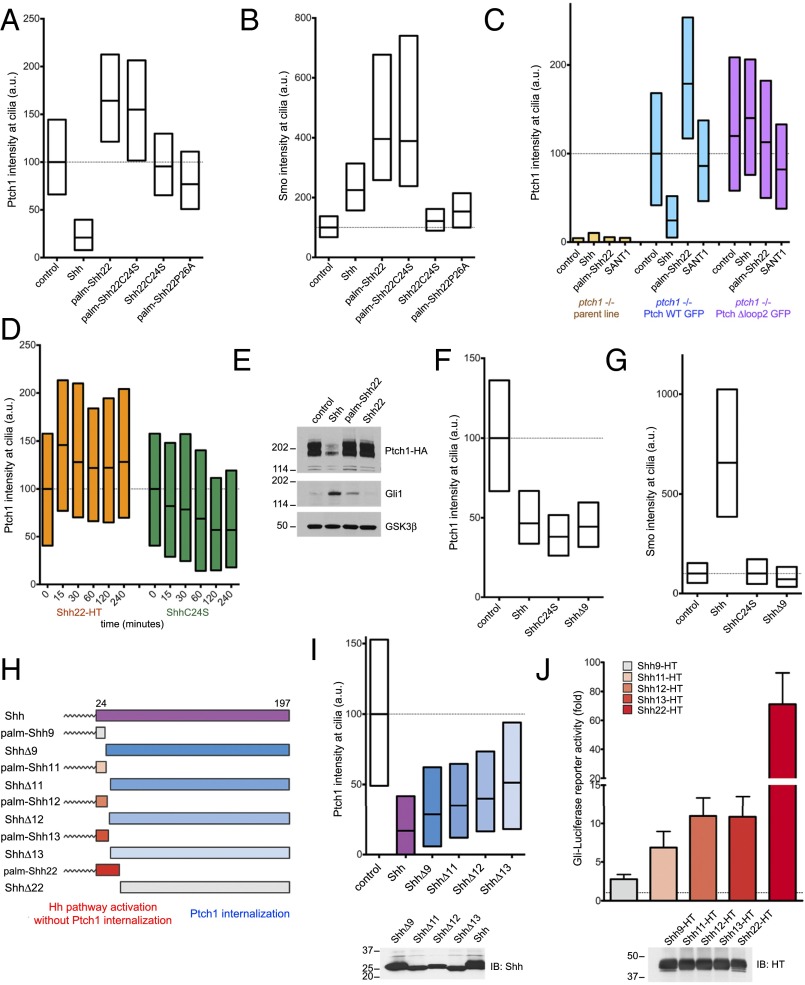
Fig. 5.
Separable parts of Shh cause Ptch1 inhibition and internalization. (A) Ptch1-null cells, stably expressing Ptch1-eGFP, were incubated with control media, Shh, or the synthetic peptides palm-Shh22, palm-Shh22C24S, Shh22C24S, and palm-Shh22P26A (5 μM each). Ptch1 localization at cilia was measured by immunofluorescence and automated image analysis (n > 300 cilia). Shh removes Ptch1 from cilia; in contrast, palm-Shh22 and palm-Shh22C24S cause Ptch1 accumulation in cilia. Shh22C24S and palm-Shh22P26A, which do not bind Ptch1, have no effect. (B) As in A, but measuring endogenous Smo at cilia. Shh, palm-Shh22, and palm-Shh22C24S recruit Smo to cilia, in contrast to Shh22C24S and palm-Shh22P26A. (C) As in A, but with cells expressing Ptch1-eGFP or Ptch1Δloop2-eGFP and incubated with control media, Shh, palm-Shh22 (5 μM), or SANT1 (1 μM). Palm-Shh22 does not cause Ptch1Δloop2 accumulation in cilia, in contrast to Ptch1. The graph showing Smo intensity at cilia in this experiment is displayed in Fig. 3B. (D) As in A, but with incubation with Shh22-HT or ShhC24S. Shh22-HT and ShhC24S have opposite effects on Ptch1 levels in cilia, with Shh22-HT causing rapid ciliary accumulation of Ptch1. (E) NIH 3T3 cells stably expressing HA-tagged Ptch1 were incubated with control media, Shh, palm-Shh22 (5 μM), or Shh22 (5 μM). Cell lysates were analyzed by SDS/PAGE and immunoblotting for Ptch1, Gli1, and GSK3β (loading control). Like Shh, palm-Shh22 activates the Hh pathway, but does not cause Ptch1 degradation, in contrast to Shh. Unpalmitoylated Shh22 is inactive. (F) As in A, but with incubation with control media, Shh, ShhC24S, or ShhΔ9. All three proteins reduce Ptch1 levels in cilia. (G) As in F, but measuring endogenous Smo at cilia. Only Shh causes Smo accumulation in cilia. (H) Schematic of constructs used to separate portions of Shh sufficient for Hh pathway activation or Ptch1 internalization. (I) As in A, but with incubation with control media, Shh, or the indicated N-terminal deletion mutants. All mutants induce Ptch1 internalization from cilia. (Lower) Equal volumes of each secreted protein were analyzed by SDS/PAGE and immunoblotting to confirm secretion. (J) N-terminal Shh peptides of various lengths were expressed in 293T cells as secreted HT fusions and were assayed for activity in Shh Light II cells. Error bars represent SD (n = 3). Equal volumes of 293T-conditioned media were analyzed by SDS/PAGE and immunoblotting. Shh11-HT, Shh12-HT, and Shh13-HT retain significant activity.