Fig. 2.
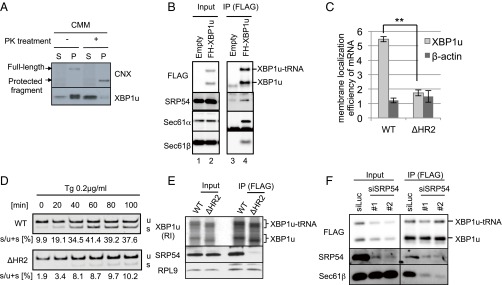
ER targeting machinery for secretory proteins interacts with XBP1u. (A) FLAG-XBP1u-HA was synthesized with RRL in the presence or absence of nontreated or proteinase K (PK)-treated CMMs. Then, CMM-associated proteins were separated from free proteins by ultracentrifugation. P, pellet; S, supernatant. Details regarding the PK treatment of microsomes are provided in Fig. S2. FLAG-XBP1u-HA was detected using an anti-FLAG antibody. (B) Coimmunoprecipitation of SRP54 or translocon components with FLAG-His-XBP1u[nonsplicing] (FH-XBP1u) transiently expressed in HEK293T cells. XBP1u and XBP1u-tRNA indicate full-length and translationally paused FH-XBP1u, respectively. IP, immunoprecipitation. (C) Membrane localization efficiencies of both XBP1u and HR2-deleted XBP1u (ΔHR2) mRNA transiently expressed in HEK293T cells. β-Actin was used as a control for cytosolic mRNA. Bars indicate SD. **P < 0.01 (n = 3) using Student’s t test. (D) Splicing of XBP1u or ΔHR2 mRNA transiently expressed in HEK293T cells was determined by RT-PCR after treatment with thapsigargin (Tg; 0.2 μg/mL) for the indicated times. s, spliced form of XBP1 mRNA; u, unspliced form of XBP1 mRNA. (E) FH-XBP1u[WT] or FH-XBP1u[ΔHR2] translated with RRL was coimmunoprecipitated with SRP54 and ribosomal protein L9 (RPL9) using anti-FLAG antibodies. XBP1u was detected by autoradiography, whereas SRP54 and RPL9 were detected by Western blotting. (F) Coimmunoprecipitation of Sec61β with FH-XBP1u[nonsplicing] transiently expressed in HEK293T cells, which were treated with siRNAs against SRP54 or luciferase (control) for 72 h until the immunoprecipitation assay.