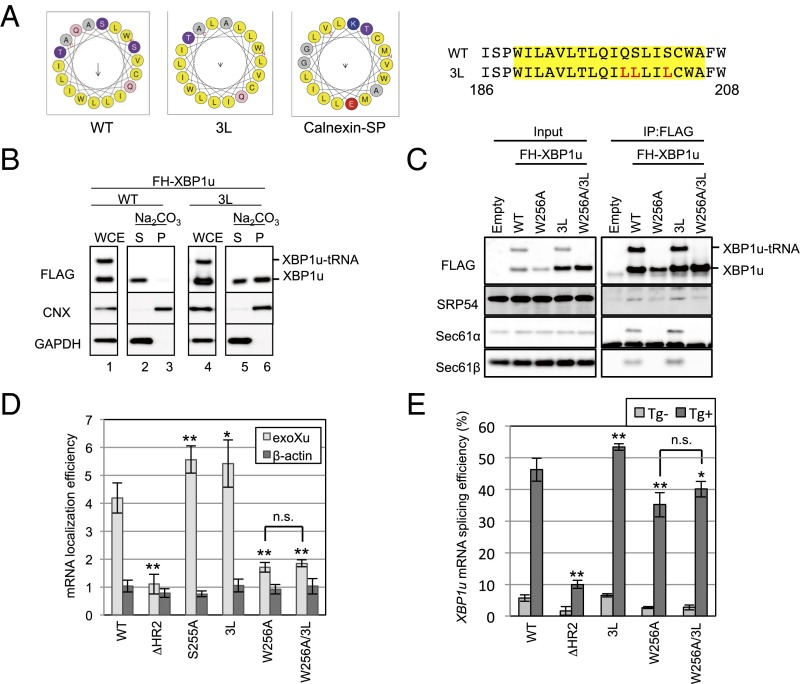
Fig. 5.
Unusual mode of ER targeting of XBP1u-RNC via SRP. (A) Helical wheel plots of amino acids in HR2 of XBP1u and the calnexin signal peptide are generated by using HeliQuest (heliquest.ipmc.cnrs.fr) (40). Wild-type and 3L mutant XBP1u are indicated as WT and 3L, respectively. (Right) Amino acid sequences of HR2 of XBP1u are shown. Sequences in the yellow rectangle are used for the helical wheel plot. Red characters in the amino acid sequences are substituted amino acids in the 3L mutant. (B) Microsomes derived from HEK293T cells transiently expressing FH-XBP1u and its variants were treated with sodium carbonate to examine the membrane-binding mode of FH-XBP1u variants. Calnexin (CNX) and GAPDH were used as controls for membrane and cytosolic proteins, respectively. (C) Coimmunoprecipitation of FH-XBP1u and its variants with indicated proteins in the cell lysate derived from HEK293T cells transiently expressing FH-XBP1u and its variants. (D) Membrane localization efficiencies of FH-XBP1u mRNA expressed in HEK293T cells were quantified as described in Fig. 2C. Bars indicate SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 using ANOVA. (E) Splicing efficiencies (percentage of XBP1s mRNA to total XBP1 mRNA) of XBP1u-ps and its variants transiently expressed in HEK293T cells. ER stress was induced with 0.2 μg/mL Tg for 1 h. Bars indicate SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 using ANOVA. n.s., nonsignificant difference.