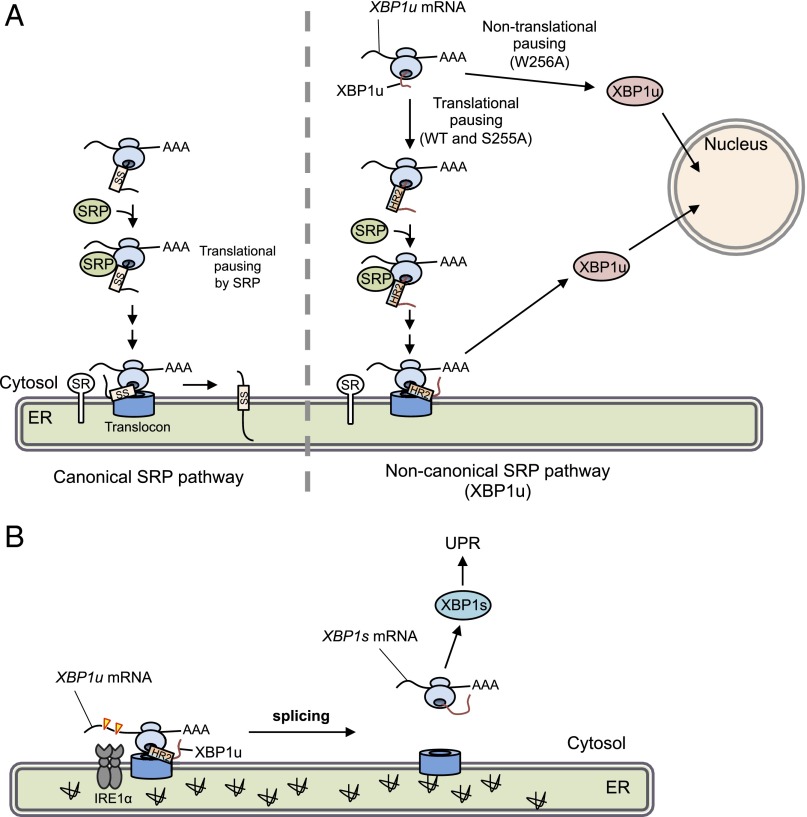
Fig. 6.
Working model of translational pausing in SRP-mediated localization of XBP1 mRNA. (A) Canonical SRP pathway (Left) and the noncanonical SRP pathway reported here (Right) are indicated. In the latter case, newly synthesized XBP1u is paused at the C terminus region of the nascent XBP1u polypeptide. Under such conditions, HR2 is located just outside of the ribosomal tunnel and is recognized by SRP. The SRP-bound RNC complex associated with its own XBP1u mRNA is recruited to the translocon via SR. After pausing, XBP1u is completely translated, but cannot be inserted into the ER owing to rejection of the translocon. Rejected XBP1u carrying NLS is quickly transported into the nucleus. In contrast, the pausing-defective mutant XBP1u[W256A], whose HR2 cannot be recognized by SRP, is translated and transported into the nucleus. SS, signal sequence, including the signal anchor. (B) Under ER stress, XBP1u mRNA associated with paused RNC on the translocon is efficiently spliced by activated IRE1α, leading to production of the active transcription factor XBP1s, which up-regulates unfolded protein response (UPR) target genes to mitigate ER stress.