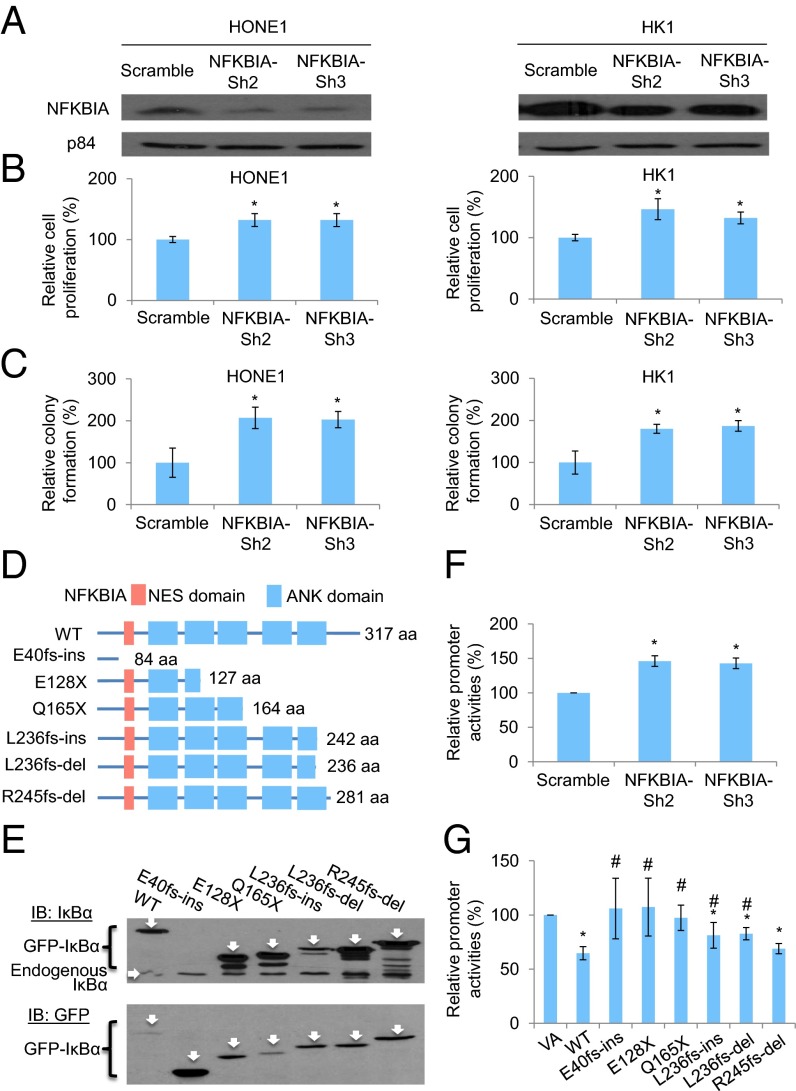
Fig. 4.
Functional investigation of NFKBIA knockdown in NPC cells and the truncating mutations identified in the IκBα protein. (A) Expression of IκBα protein in both NPC HONE1 and HK1 cell lines after knockdown with two independent sets of shRNA knockdown oligonucleotides. (B) Cell proliferation assay of HONE1 and HK1 cells after NFKBIA knockdown. The relative cell proliferation rate was compared with the corresponding scramble control. (C) Colony formation assay of HONE1 and HK1 cells after NFKBIA knockdown. (D) Schematic diagram illustrates the truncated site of each mutant of IκBα protein by in silico analysis. NES, nuclear export signal. (E) Western blot results illustrate the protein size of each mutant. The IκBα was tagged with an N-terminal GFP tag. The GFP-IκBα-WT (61.9 kDa), GFP-E40fs-ins (35.659 kDa; this mutant lost the epitope for the IκBα antibody recognition; therefore, it cannot be detected by the IκBα-specific antibody), GFP-E128X (41.68 kDa), GFP-Q165X (45.49 kDa), GFP-L236fs-ins (53.84 kDa), GFP-L236fs-del (53.04 kDa), and GFP-R245fs-del (57.85 kDa) were detected by specific antibody against the (Upper) IκBα and (Lower) GFP. IB, immunoblot. (F) NF-κB–specific dual luciferase promoter assay in the 293T cell lines with NFKBIA knockdown. (G) NF-κB–specific dual luciferase promoter assay in the 293T cell line with expression of IκBα-WT and mutants. This cell line has constitutive NF-κB activation. The relative promoter activity value was compared with the VA control. The data shown in B, C, F, and G represent means ± SD (n = 3). *Statistical significance (P < 0.05) compared with the scramble control or VA; #statistical significance (P < 0.05) compared with the WT.