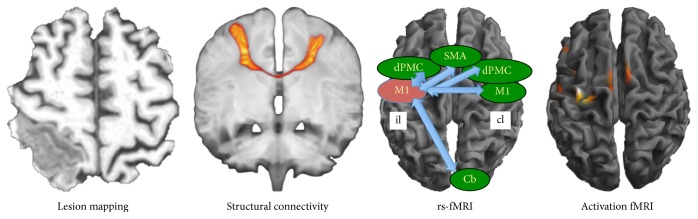
Figure 2.
Two structural and two functional imaging methods applied in monitoring and predicting hand-motor outcome after stroke. From left to right: lesion mapping on a T1 weighted imaging dataset; diffusion-weighted imaging measuring structural connectivity, demonstrated here with probabilistic tracking between the bilateral primary motor cortices; resting-state fMRI (rs-fMRI) assessing functional connectivity between different regions of interest (Cb: cerebellar anterior hemisphere; dPMC: dorsal premotor cortex; SMA: supplementary motor area); and activation fMRI during active grip strength task with the affected right hand.