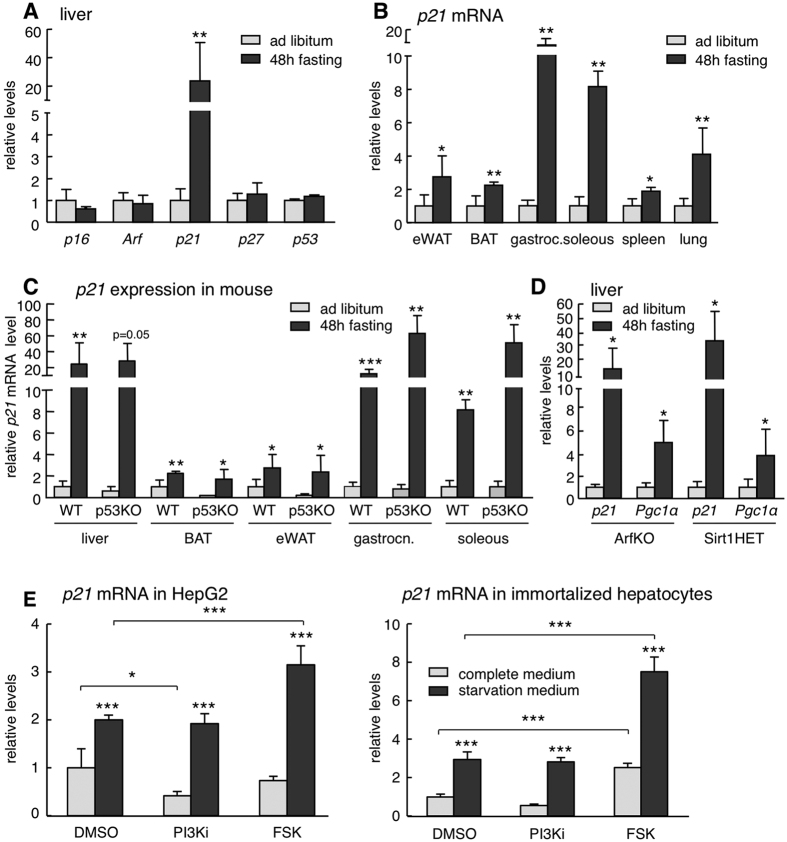
Figure 1. Characterization of fasting-induced p21 upregulation.
(A) Relative mRNA expression of the indicated tumor suppressor genes in the liver after 48 h fasting compared to ad libitum fed mice (n = 4 per group, males, 12 weeks old). (B) Relative p21 mRNA levels in epididymal white adipose tissue (eWAT), brown adipose tissue (BAT), gastrocnemius, soleous, spleen and lung of mice after 48 h fasting or ad libitum feeding (same mice as in panel A). (C) Relative p21 mRNA levels in the indicated tissues of ad libitum fed and 48 h fasted wild type (WT) or p53KO mice (n = 4 per group, males, 12 weeks old). (D) Relative p21 and Pgc1α expression in the liver of ArfKO and Sirt1HET mice after 48 hours fasting or ad libitum feeding (n = 4 per group, males, 12 weeks old). The fasting-induced gene Pgc1α was used as control. (E) Relative p21 mRNA levels in HepG2 (human hepatocellular carcinoma) cells (left) or primary large-T immortalized mouse hepatocytes (right) cultured for 24 h in complete medium (DMEM + 10%FBS) or starvation medium (glucose-free and serum-free DMEM) and treated for 5 h with DMSO, 10 μM CNIO PI3K inhibitor (PI3Ki) or 10 μM forskolin (FSK). The experiment was performed twice with similar results and each time in three biological replicates. Data correspond to one experiment (n = 3). Levels of mRNA were normalized to β-actin, except for muscle that is normalized to Gapdh. Values correspond to average ± s.d. Statistical significance was determined by the unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test (panels A to D) or by two-way ANOVA and Bonferroni post-hoc test (panel E): *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.