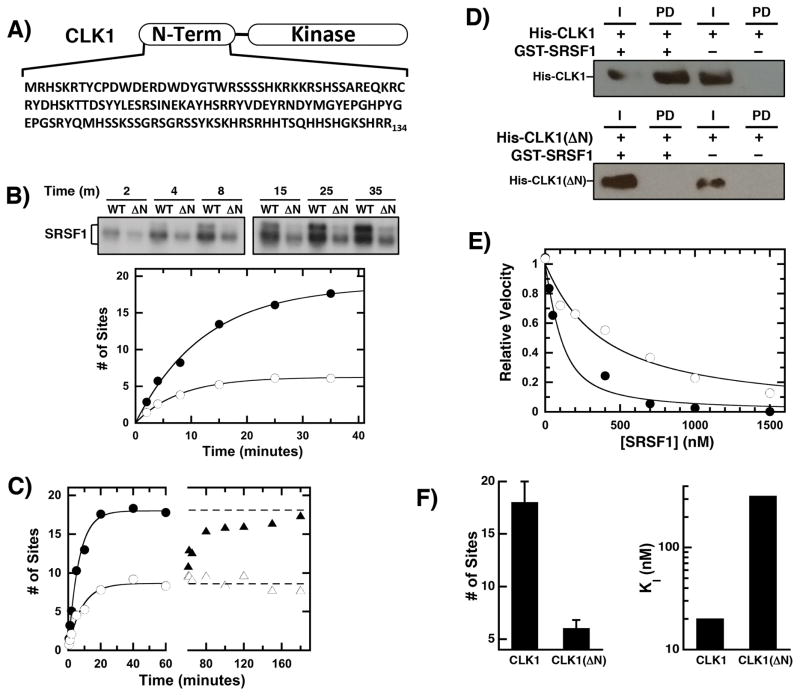
Figure 1. CLK1 N-terminal sequences regulate RS domain binding & phosphorylation.
A) CLK1 N-terminus. B) Phosphorylation of SRSF1 (0.15 μM) using 32P-ATP (50 μM) and 50 nM CLK1 or CLK1(ΔN) is monitored by SDS-PAGE autoradiography. Time-dependent phosphorylation is fit with an amplitude and rate constant of 18 sites and 0.08 min−1 for CLK1 (●) and 6 sites and 0.13 min−1 for CLK1(ΔN) (○), respectively. C) Enzyme Doping. SRSF1 (60 nM) is phosphorylated using 30 nM CLK1 (●) and CLK1(ΔN) (○) and after 60 minutes, additional CLK1 (▲) or CLK1(ΔN) (△) are added to the CLK1(ΔN) reaction. D) The interaction of His-tagged CLK1 and CLK1(ΔN) with GST-SRSF1 is monitored on g-agarose beads using an anti-His antibody in pull-down assays. I = Input, PD = pull down. E) Competition Experiments. The phosphorylation of 50 nM SR(ΔRRM1) is monitored with varying amounts SRSF1 using CLK1 (●) and CLK1(ΔN) (○). The data are fit to equation (1) to obtain appKI of 50 and 320 nM for CLK1 and CLK1(ΔN). F) Bar Graphs. Total number of phosphorylation sites and true binding affinities of SRSF1 are plotted for CLK1 and CLK1(ΔN). The error bars for the total number of sites were obtained from triplicate measurements.