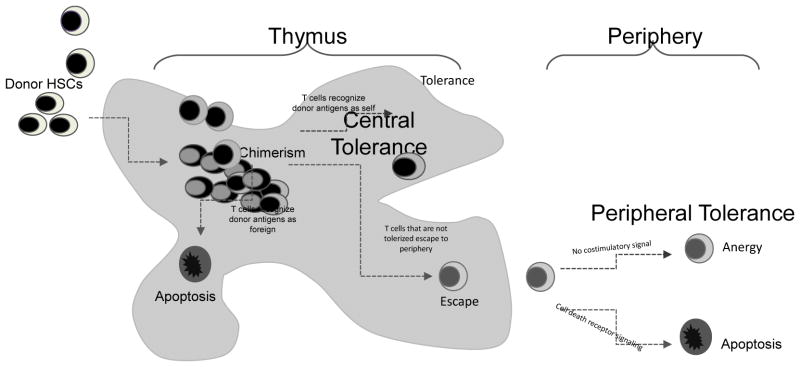
Figure 1. Schematic of mechanisms of HSC-induced tolerance.
Donor HSCs home to the recipient thymus, where they integrate with recipient thymic cells and develop donor/recipient chimerism. The result of chimerism is that central tolerance mechanisms ensue allowing mature T cells to develop that can recognize donor antigens as self (tolerized). T cells that recognize donor antigens as foreign undergo apoptosis. T cells that escape to the periphery undergo peripheral tolerance mechanisms that result in either anergy (in the absence of costimulation) or apoptosis (in the presence of costimulation).