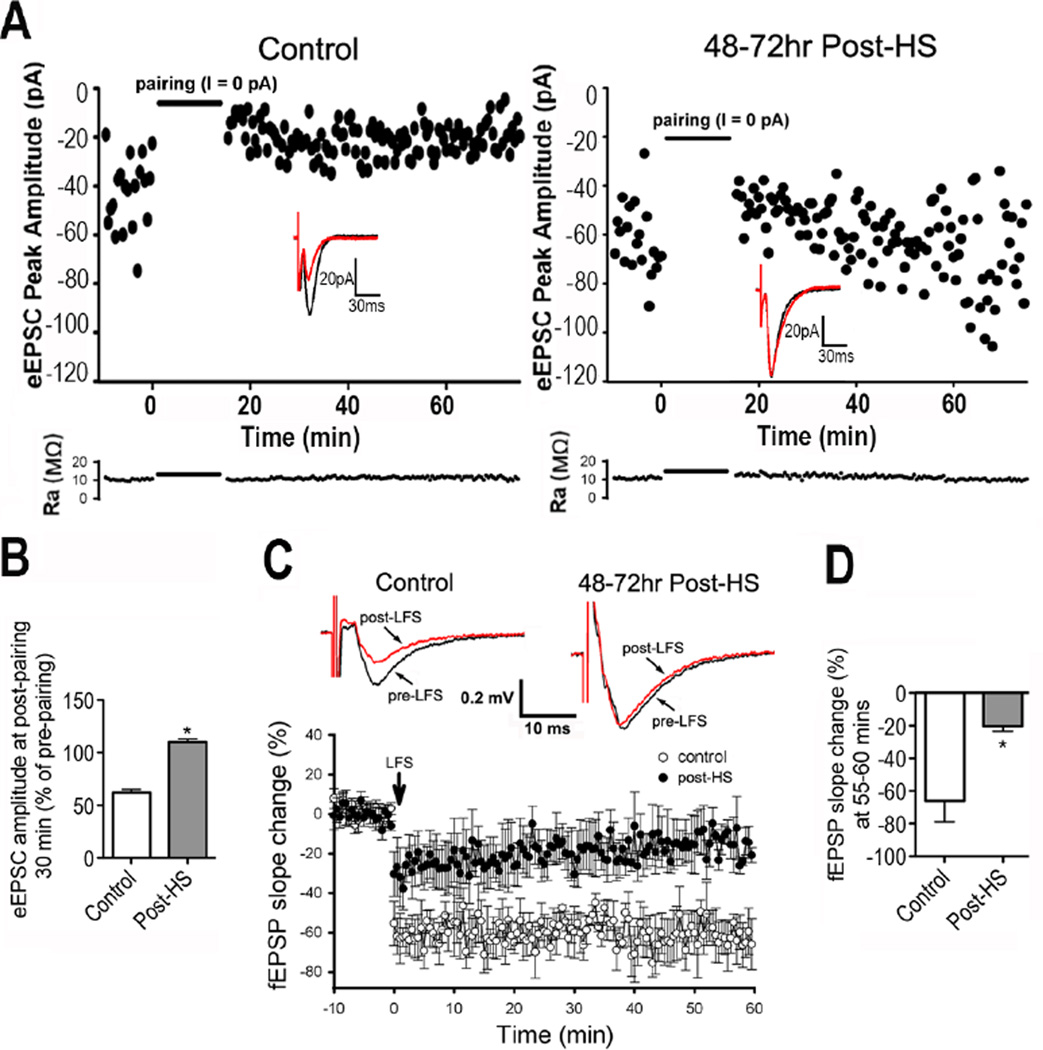
Figure 3. LTD is attenuated 48 hours post-HS.
A) Time course of eEPSC amplitude in CA1 pyramidal neurons with pairing protocol shows attenuation in LTD 48–72 hours post-HS (right) compared with control (left). Inserts are representative traces before and 30 min post-LFS. Lower panel shows the time course of access resistance during LTD recording period. B) Summarized eEPSC amplitude changes in slices before pairing and 30 min post-pairing for control and post-HS rats; n=6 slices/group, p=0.02 by t-test. C) Representative averaged field (f)EPSP traces recorded in CA1 pyramidal neurons from control (top left panel) and post-seizures (in vivo seizures at P10) (Top right panel). Time course of LFS induced fEPSP change shows attenuated LTD in slices from rats post-HS compared to controls (lower panel). D) Quantification of fEPSP slope percent change from pre-LFS averaged over minutes 55–60 post-LFS in slices taken 48–72 hours post-HS and from age-matched controls (n=6, p=0.006 by t-test). Slopes were significantly lower in controls than in post-HS slices. Data is represented as mean±SE.