Fig. 5.
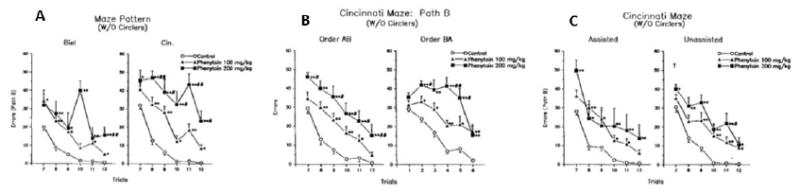
CWM errors (Mean ± SEM) in offspring of pregnant rats treated by gavage on E7-18 with phenytoin free base and tested under visible light. The experiment evaluated separate offspring from each litter in one of three factors influencing performance: (A) maze complexity (BWM vs. CWM), (B) path order (path A then B, or path B then A) where the Y-axis shows path-B errors, and (C) assistance type (assisted vs. unassisted escape). (A) Maze complexity was is compared on path-B of the Biel or Cincinnati versions but in the same apparatus: Left, BWM configuration; Right, CWM configuration. These data provide evidence that the CWM better differentiated the groups compared with the BWM. Data are mean ± SEM per trial. From (Vorhees et al., 1991a). (B) The part of the experiment compared different offspring from each litter on path order for effects on Path-B performance. Left, Path-B errors when path order was A then B; Right, Path-B errors when the path order was B then A (Vorhees et al., 1991a). (C) In this part of the experiment different offspring from each litter were used to compare the type of escape assistance used for those that reached the 5 min time limit. Left, errors using assisted escape; Right, errors using unassisted escape (Vorhees et al., 1991a).
