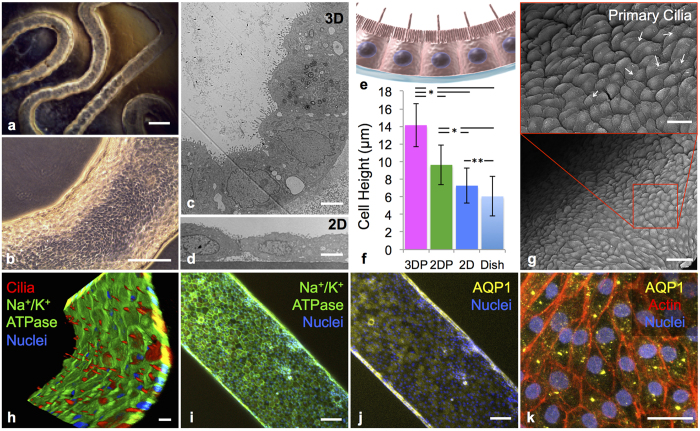
Figure 2. 3D proximal tubule morphology and molecular markers.
(a) A phase contrast image of a mature 3D PT construct taken at 6 weeks, scale bar = 500 μm, (b) phase contrast image of the 3D PT construct at 6 weeks, scale bar = 250 μm, (c) TEM image of the PTECs within the tubule at 5 weeks, scale bar = 5 μm, (d) TEM image of the PTECs grown on a 2D dish coated with ECM with no perfusion, scale bar = 5 μm, (e) schematic view of the columnar epithelium seen in native tissue, in which PTECs pack together closely and exhibit a dense brush border on the apical side, tight junctions, and a solid basement membrane, (f) PTEC cell height as measured from TEM images of the 3D PT constructs (3DP) as well as three 2D controls (2DP = PTECs on ECM in 2D with perfusion, 2D = PTECs on ECM in 2D not perfused, Dish = bare tissue culture dish not perfused), *p < 0.001, **p < 0.02, (g) SEM images at low (scale bar = 50 μm) and higher (scale bar = 20 μm) magnifications showing a confluent layer of PTECs within the 3D PT, white arrows highlight the presence of primary cilia at a density of one per cell, (h) 3D rendering of a partial tubule showing the apical side, which highlights the primary cilia (red), scale bar = 20 μm, (i) image of the PT highlighting the presence of Na/K ATPase in green, scale bar = 100 μm, (j) image of the 3D PT highlighting the presence of AQP1 in yellow, scale bar = 100 μm, (k) high magnification view of the image in (j) highlighting actin in red and showing AQP1 in yellow, scale bar = 20 μm.