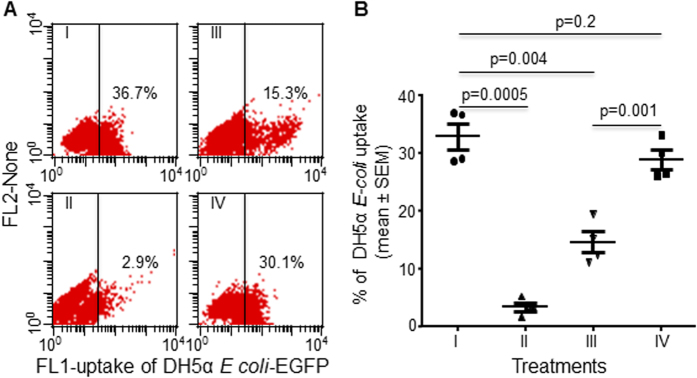
Figure 4. Ligation of LILRB4 significantly suppressed Fc receptor-dependent uptake of antibody-opsonised.
E. coli by differentiated THP-1 cells. (A) Representative dot plot showing uptake of Ab opsonized EGFP-expressing DH5α E-coli particles by 36.7% of PMA-differentiated THP-1 cells (I) that was reduced by 90% when surface FcγRI was blocked by pre-incubating cells with 20 μg/ml anti-FcγRI mAb (II), but not by cells pre-incubated with negative control IgG1 mAb, indicating Fc-receptor dependent endocytosis/phagocytosis (n = 4). Ligation of LILRB4 with mouse anti-LILRB4 mAb followed by goat anti-mouse secondary Ab reduced uptake of Ab opsonized EGFP-expressing DH5α E-coli particles by >50% (III) when compared with non-ligated cells (I). Ligation of control mouse anti-MHC-I mAb (IV) or negative control mouse mAb had little effect on uptake, confirming specific LILRB4-mediated suppression. (B) Summary analysis of 4 independent experiments presenting mean percentages (±SEM) showing that numbers of PMA- differentiated THP-1 cells that took up Ab-opsonized EGFP-expressing DH5α E-coli particles were significantly less if cells were pre-incubated with anti-FcγRI mAb (p = 0.0005), and markedly less following Ab ligation of surface LILRB4 (p = 0.004), but not Ab ligation of MHC-I (p = 0.2).