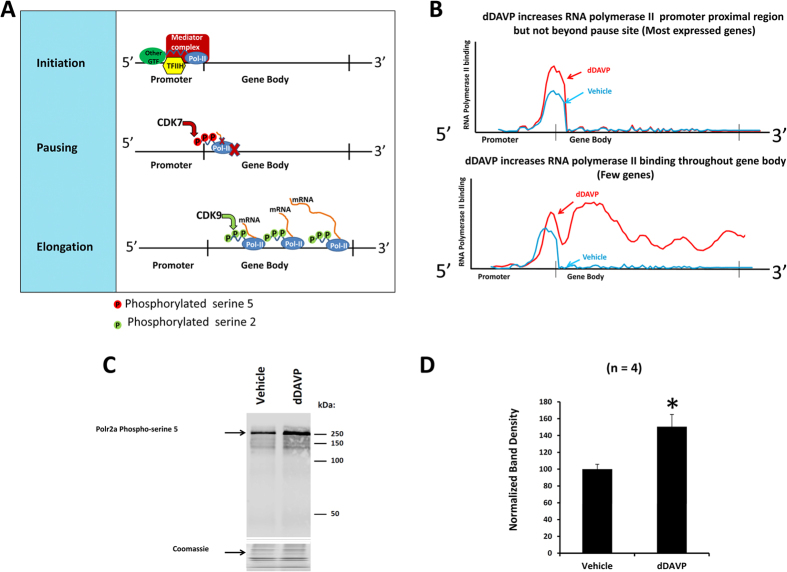
Figure 4. Cartoons showing simplified views of transcriptional regulation and the effects of vasopressin on transcription in mpkCCD cells.
(A) Three elements of transcription are initiation (top), pausing (middle) and elongation (bottom). Initiation involves localization of the RNA polymerase II complex (Pol-II) at the TSS guided in part by General Transcription Factors (GTFs) including TFIIH and the Mediator Complex. At initiation, Polr2a is phosphorylated at Serine-5 positions in the 52 heptad repeats making up the COOH-terminal domain by cyclin-dependent kinase 9 (CDK9). Most genes exhibit pausing of Pol-II in the promoter proximal region indicated by the red X. Pause release occurs in part because of Polr2a phosphorylation at Serine-2 positions of the COOH-terminal heptads by CDK7, promoting elongation. During elongation, Polr2a-specific phosphatases dephosphorylate at Serine-5 positions. (B) The two types of vasopressin-mediated regulation exhibited in this study. In most expressed genes (top), vasopressin increased RNA polymerase II binding only in the promoter proximal region. This pattern and the increase in Ser5 phosphorylation in Polr2a support the conclusion that vasopressin signaling triggers a broad increase in transcriptional initiation for most genes. For a few genes (bottom), vasopressin increased RNA polymerase II binding throughout the gene body pointing to highly selective regulation of elongation. (C) Immunoblot for Polr2a phosphorylated at Ser5 positions in COOH-terminal domain shows increase with vasopressin. Coomassie-stained gel shows identical input protein. (D) Mean band density for pSer5-Polr2a was significantly increased over 4 replicates. *P < 0.05, t-test.