Figure 5.
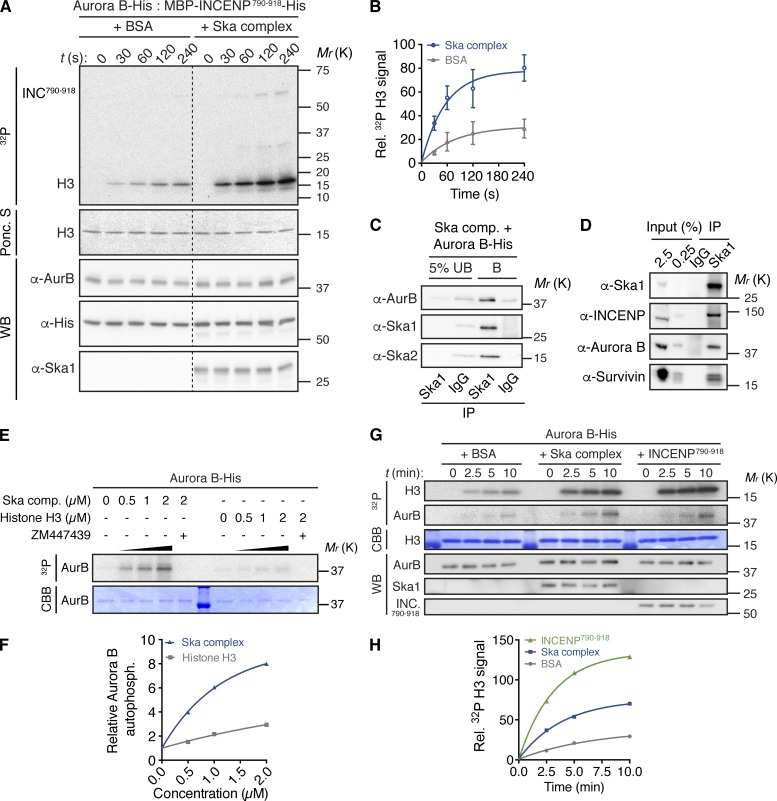
The Ska complex promotes the catalytic activity of Aurora B in vitro. (A) Time course kinase assay with Aurora B–His and MBP–INCENP790–919–His preincubated with Ska complex or equimolar amounts of BSA, as control, before addition of histone H3 and γ-[32P]ATP. (B) Quantification of histone H3 32P signals from A. Signals were normalized to H3 and Aurora B protein levels monitored by Ponceau S staining (Ponc. S) and Western blotting (WB), respectively. Signal intensities are expressed relative to the first time-point. Data represent mean ± SD (three experiments). (C) Aurora B–His was incubated with recombinant Ska complex before pull-down with beads coupled to anti-Ska1 antibody or control antibody (IgG). UB, unbound fraction; B, bound fraction. (D) Immunoprecipitates (IP) from mitotic HeLa S3 cell extracts, obtained using anti-Ska1 antibodies or control antibodies (IgG), analyzed by WB. (E) Aurora B–His was preincubated with Ska complex (comp.) or histone H3, as control, before incubation with γ-[32P]ATP. Aurora B autophosphorylation is visualized by autoradiography (32P) and Aurora B levels by Coomassie Brilliant Blue (CBB) staining (see Fig. S5 G for uncropped results). (F) Quantification of Aurora B autophosphorylation signals from E (one experiment). Signal intensities are expressed relative to the first concentration. (G) Time course kinase assay with recombinant Aurora B–His preincubated with Ska complex, equimolar amounts of MBP–INCENP790–919–His or BSA, as control, before addition of histone H3 and γ-[32P]ATP. (H) Quantification of Aurora B kinase activity as in B (one experiment).