Figure 1.
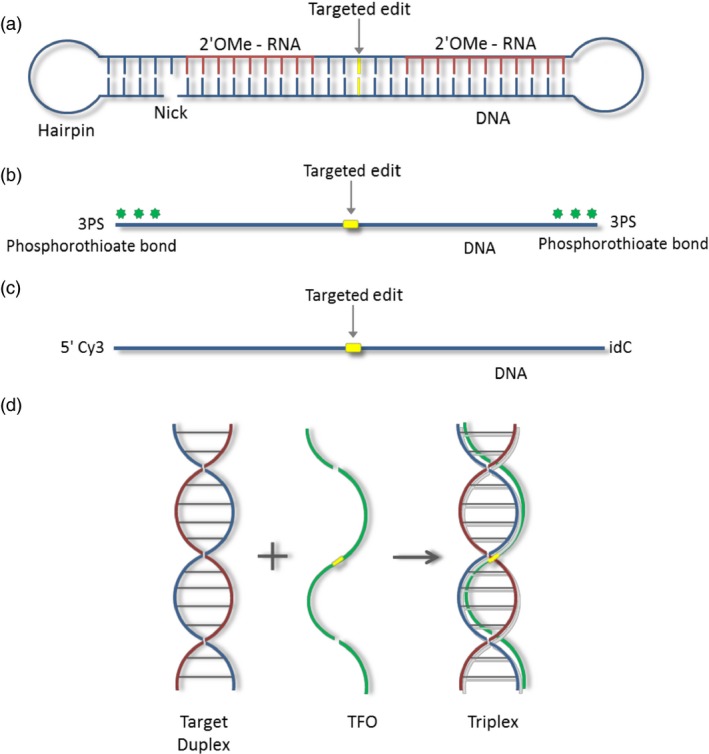
Oligonucleotide designs. (a) chimeraplast schematic showing regions of DNA (blue) and RNA (red; 2′‐O‐methyl modified), a nick and hairpin (total chimeraplast is ~68 nucleobases). (b) A single‐stranded oligonucleotide modified with 3PS (3 phosphorothioate bonds) at both the 5′ and 3′ ends (total oligonucleotide length is 41, 101 or 201 nucleobases). (c) A single‐stranded oligonucleotide modified with a Cy3 dye at the 5′ end and a reverse base (idC) at the 3′ end (total oligonucleotide is 41 nucleobases). (d) Triplex‐forming oligonucleotide (TFO). The target duplex homopurine and homopyrimidine strands are shown in blue and red. The TFO, which binds the homopurine strand, is indicated in green. The location of the targeted nucleotide in all oligonucleotides is shown in yellow.
