Fig. 4.
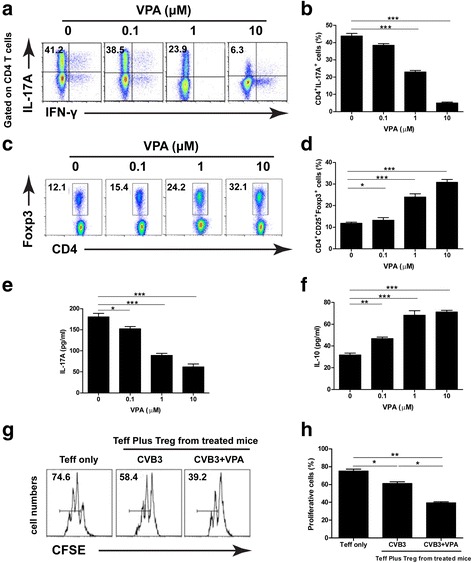
VPA influences Th17 and Treg cells differentiation in vitro and in vivo. Purified naive CD4+ T cells from normal BALB/c mice were cultured with different concentrations of VPA under Th17 or Treg cells-polarizing conditions. The differentiations of Th17 cells or Treg cells were analyzed by Flow cytometry (a and c, left panels). Bar graph shows the representative percentage of in vitro-differentiated Th17 cells or Treg cells (b and d, right panel). Spleen CD4+ T cells isolated from mice 6d after CVB3 infection were treated with PBS or VPA for 24 h ex vivo, the supernatants were collected and ELISA was performed to determine the level of IL-17A (e) and IL-10 (f). CD4+CD25+ T cells isolated from CVB3 infected mice treated with VPA or vehicle were isolated on day 6 and co-cultured with CFSE-labeled CD4+CD25−T effector (Teff) cells from naïve mice on anti-CD3/CD28 mAb coated plates. The suppression was assayed by Flow cytometry for dilution of CFSE in gated Teff cells (g and h). Results are presented as the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001
