Fig. 3.
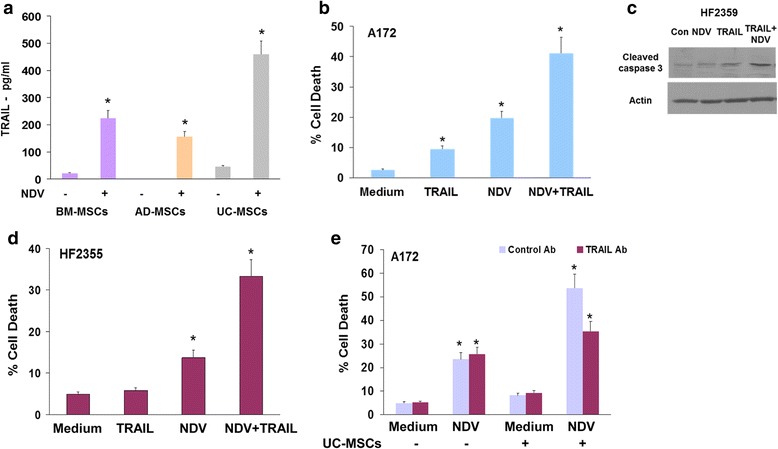
NDV-infected MSCs exert an increased cytotoxic effect on glioma cells and GSCs via the secretion of TRAIL. MSCs were infected with NDV (2 MOI) for 2 days and the levels of secreted TRAIL was determined by ELISA (a). Treatment of A172 (b), the HF2359 GSCs (c) or the HF2355 (d) with TRAIL (25 ng/ml) and NDV (1 MOI) induced an increased effect on cell death. The addition of a neutralizing anti-TRAIL antibody (5 μg/ml) prior to NDV infection abrogated the increased cytotoxic effect of conditioned medium derived from UC-MSCs infected with NDV (e), whereas it did not affect the cytotoxic effect of NDV infection of glioma cells. The results are presented as mean ± SE and represent three different experiments. * p < 0.001 (control vs. infected cells; NDV + TRAIL vs. NDV and TRAIL; control antibody vs. anti-TRAIL antibody). AD adipose tissue, BM bone marrow, GSC glioma stem cell, MSC mesenchymal stromal cells cell, NDV Newcastle disease virus, NSC neural stem cell, TRAIL TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand, UC umbilical cord
