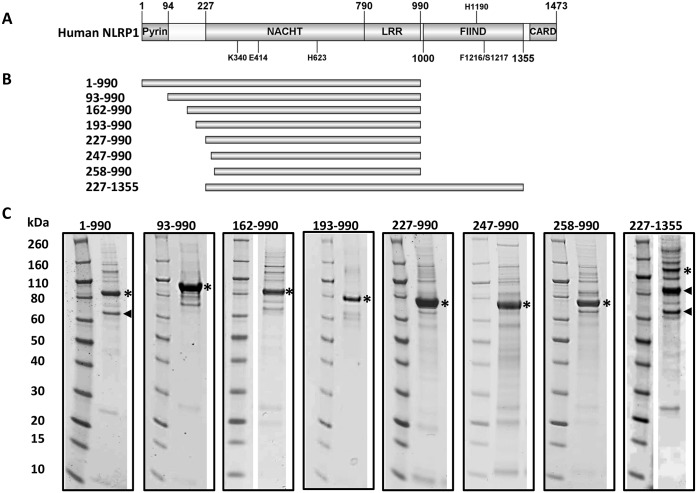
Fig 1. Domain organisation and expression screen of human NLRP1.
(A) Human NLRP1 domain organisation; black lines indicate some of the key residues reported to be important for protein function. K340 and E414 belong to the Walker A and Walker B motifs, respectively and are important for ATP processing. H623 is a conserved residue across all the NLRs, the correspondent residues in NLRC4 and in Apaf1 are involved in stabilising the ADP-bound conformation. H1190, F1216 and S1217 are reported to be important for the auto-proteolysis of the FIIND domain. (B) Schematic representation of the soluble constructs produced in insect cells. The boundaries of each construct are indicated on the left. (C) SDS-gels of the recombinant proteins from insect cells after the first metal affinity purification step. A black star indicates the protein of interest and a black arrow heads indicates proteolytic degradation products.