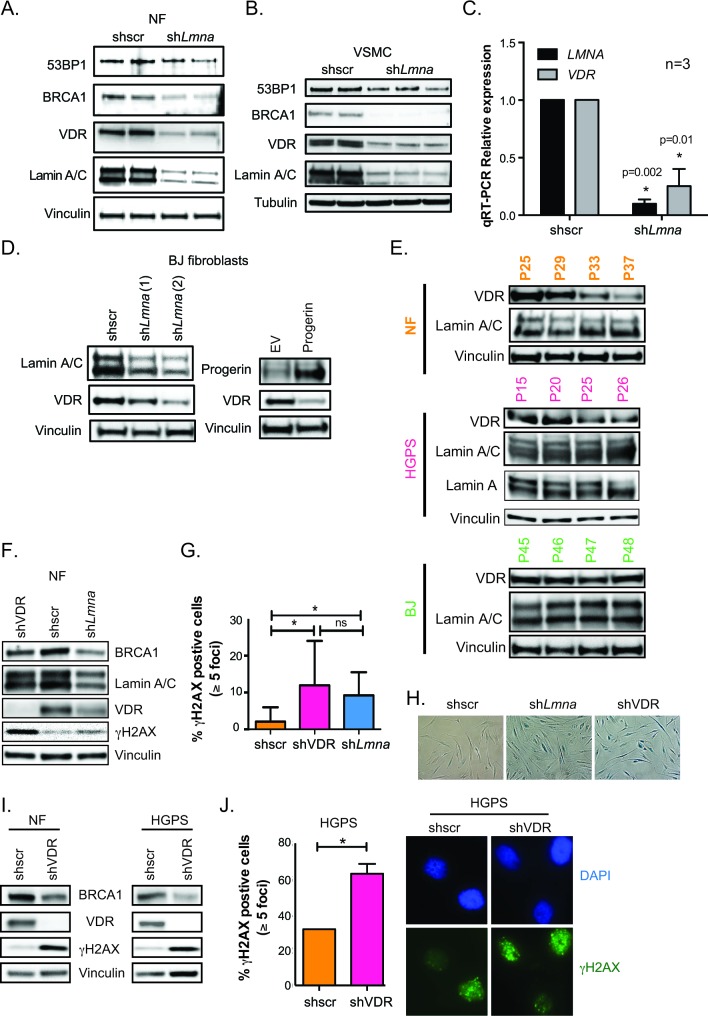
Figure 1. VDR deficiency in cells with disrupted nuclear lamina.
A. Human NF lentivirally transduced with shRNA targeting lamin A/C (shLmna) or scrambled (shscr), and processed for immunoblotting (2 independent transductions). Vinculin is loading control. B. The same experiments as in (A) performed in human VSMC. Tubulin is loading control. C. Relative expression of LMNA and VDR transcripts by qRT-PCR in VSMC after depletion of lamin A/C or VDR. Results are mean±sem of 3 biological repeats. D. BJ fibroblasts were lentivirally transduced with 2 independent shRNAs targeting lamin A/C (left panels) or retrovirally transduced with progerin (right panels) and processed for immunoblotting. E. Different human fibroblasts (BJ, NF and HGPS) were collected at increasing passages in culture to monitor levels of VDR and lamin A/C by western blot. F. NF were lentivirally transduced with shscr, shLmna, or shRNA targeting VDR (shVDR) and processed for immunoblotting. G. Immunofluorescence (IF) with γH2AX antibody in NF depleted of VDR, lamin A/C, and control. Quantitated percentage of cells with more than 5 γH2AX foci. Graph represents mean±sem of 3 independent experiments. H. Images show how depletion of lamin A/C or VDR leads to accumulation of β-galactosidase positive cells, a marker of senescence (after 2 weeks). I. NF and HGPS cells were depleted of VDR and levels of BRCA1, VDR, and γH2AX monitored by immunoblotting. J. IF performed in HGPS depleted of VDR (shVDR) and control (shRNA) and percentage of γH2AX-positive cells quantitated. Images of IF showing accumulation of γH2AX in HGPS cells depleted of VDR. *p value of statistical significance (*p ≤ 0.05).