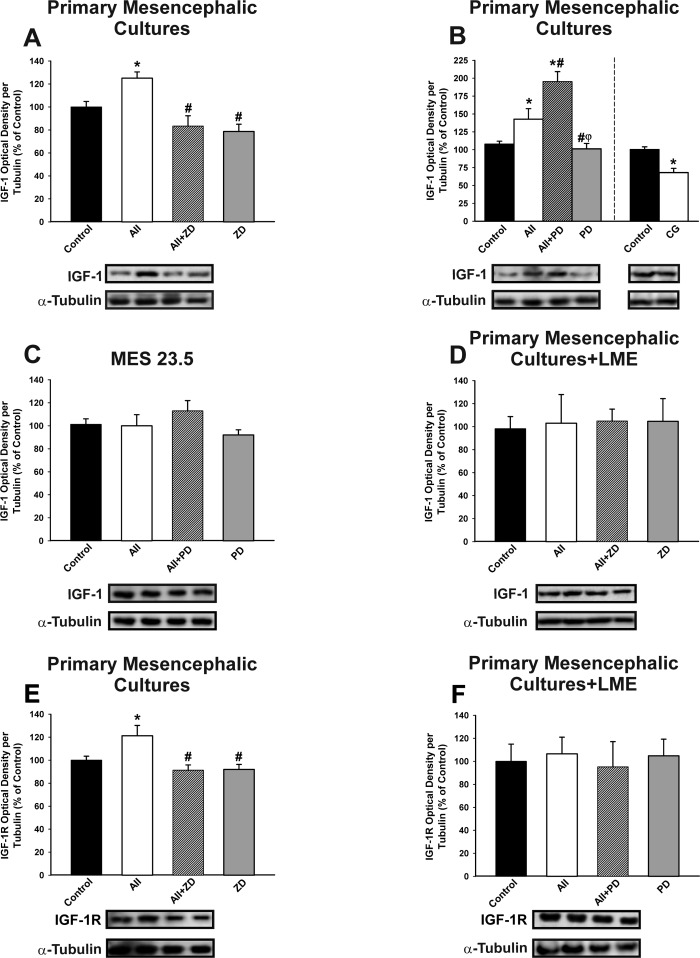
Figure 4. Effect of treatment with AII (100 nM) on IGF-1 (A-D) and IGF-1 receptor (IGF-1R; E-F).
Western blot analysis of changes induced by treatment with AII in expression of IGF-1 and IGF-1R in primary mesencephalic cultures A., B., E., the dopaminergic neuron cell line MES 23.5 C. and primary mesencephalic cultures lacking microglial cells (i.e. treated with LME) D., F. The AII-induced increase in IGF-1 and IGF-1R expression was inhibited by the AT1 receptor antagonist ZD-7155 and the AT2 agonist CG-42112A, and enhanced by the AT2 receptor antagonist PD-123319. However, treatment with AII did not induce significant changes in IGF-1 and IGF-1R in the absence of microglia C., D., F. Protein expression was measured relative to the α-tubulin band value. The results were normalized to the values for controls (100%). Data are means ± SEM. *p < 0.05 relative to controls; #p < 0.05 relative to AII-treated group; φp < 0.05 relative to AII+PD group. One-way ANOVA followed by Holm Sidak post-hoc test. AII, angiotensin II; CG, AT2 agonist CG-42112A; LME, L -leucine methyl ester; PD, AT2 antagonist PD-123319; ZD, AT1 antagonist ZD-7155.