Figure 2. TRIM44 increases the motility and invasive properties of non-small cell lung cancer cells.
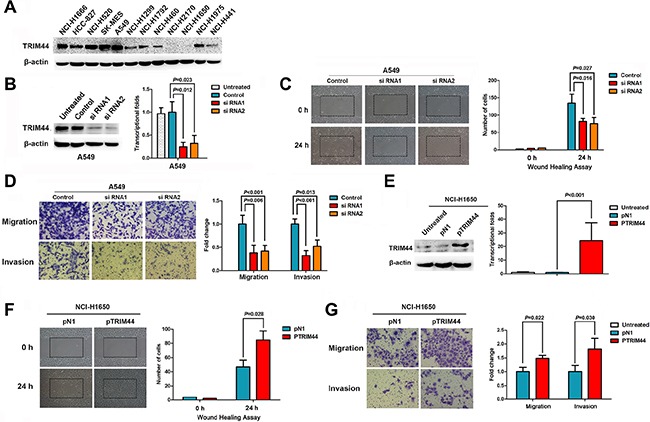
(A) Expression of TRIM44 in 12 lung cancer cell lines was examined by western blotting. β-actin was used as a loading control. (B) TRIM44 expression was confirmed by immunoblotting and real-time qRT-PCR. TRIM44 expression in A549 cells was reduced markedly by RNA interference. P values were calculated using Student's t-test (C) Wound healing assays were used to investigate the migration of A549 cells. P values were calculated using Student's t-test (D) Both invasion and migration of A549 cell lines (and their derivatives) were measured in a Transwell assay. P values were calculated using Student's t-test. (E) Immunoblot and real-time qRT-PCR analysis of TRIM44 protein and mRNA expression, respectively, in NCI-H1650 cells transfected with pDoubleEx-EGFP-TRIM44 (pTRIM44) or pDoubleEx-EGFP-N1 empty vector (pN1). P values were calculated using Student's t-test. (F) Wound healing assays were used to examine the migration of NCI-H1650 cells. P values were calculated using Student's t-test. (G) The migration and invasion of NCI-H1650 cell lines (and their derivatives) were measured in a Transwell assay. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM (n = 3). P values were calculated using Student's t-test.
