Figure 4. Effects of TRIM44 on NSCLC cell viability in vitro and in vivo.
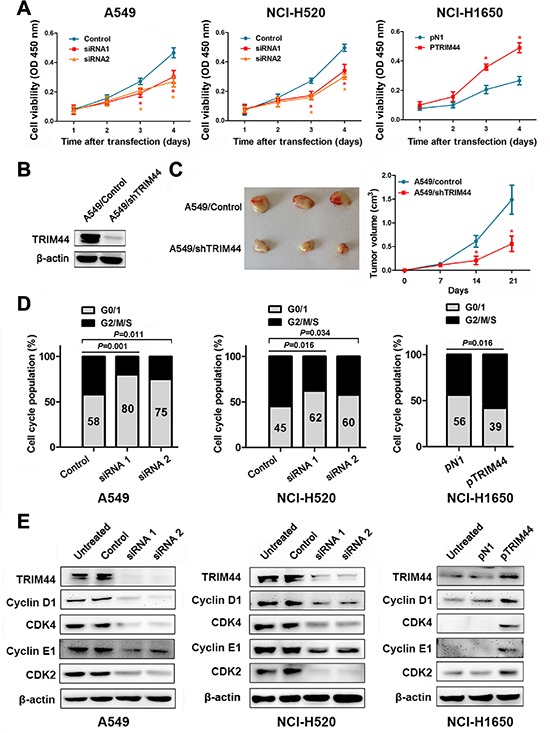
(A) CCK-8 assays were used to examine changes in the proliferation rate of NSCLC cells at different time intervals (from 24 to 96 h). Data are expressed as the absorbance (mean ± SEM) for each group (n = 3). *P < 0.05 (Student's t-test). (B) Western blot analysis of TRIM44 and β-actin expression (loading control) in A549 cells stably transfected with shControl and shTRIM44 lentiviruses. (C) Knockdown of TRIM44 led to a marked reduction in tumor volume. The volume of tumors formed by stable A549/control or A549/shTRIM44 clones in NOD-SCID mice was measured weekly using a Vernier caliper. Left panel: gross view of isolated tumors. Right panel: shows mean ± SEM (n = 10) volume per group at each time point. *P < 0.05 (Student's t-test). (D) TRIM44 is involved in cell cycle progression. The cell cycle was examined by flow cytometry. P values were calculated using Student's t-test. (E) Representative western blot showing the effects of TRIM44 on the expression of cyclins and CDKs in NSCLC cells. All experiments were performed in triplicate, with three technical replicates.
