Figure 6. H2O2-induced increases in ROS that result in defective CD34-positive cells are partially reversed by N-acetyl-L-cysteine.
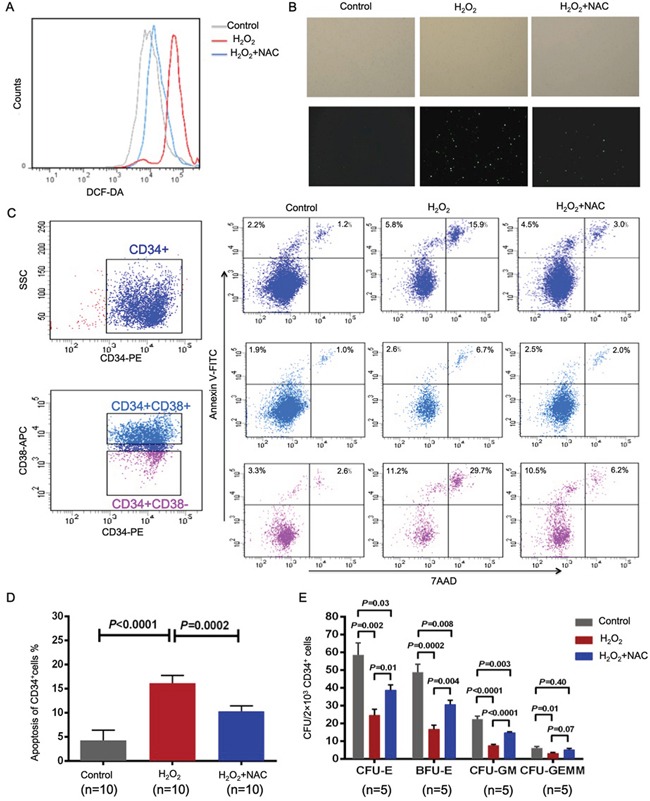
To further investigate the effect of oxidative stress on normal post-transplant hematopoiesis, CD34-positive bone marrow cells from subjects with good graft function were treated with H2O2 with or without N-acetyl-L-cysteine. The cells were then stained with DCFH-DA and analyzed by flow cytometry A. or fluorescence microscopy B. to detect intracellular ROS. H2O2 treatment of CD34-positive bone marrow cells from subjects with good graft function dramatically increased the percentage of apoptosis cells, whereas N-acetyl-L-cysteine partially but significantly restored apoptosis C, D. and the defective colony-forming unit plating efficiency E. of CD34-positive bone marrow cells.
