Figure 5. KLF4 transactivated CRYAB gene expression by binding the promoter region.
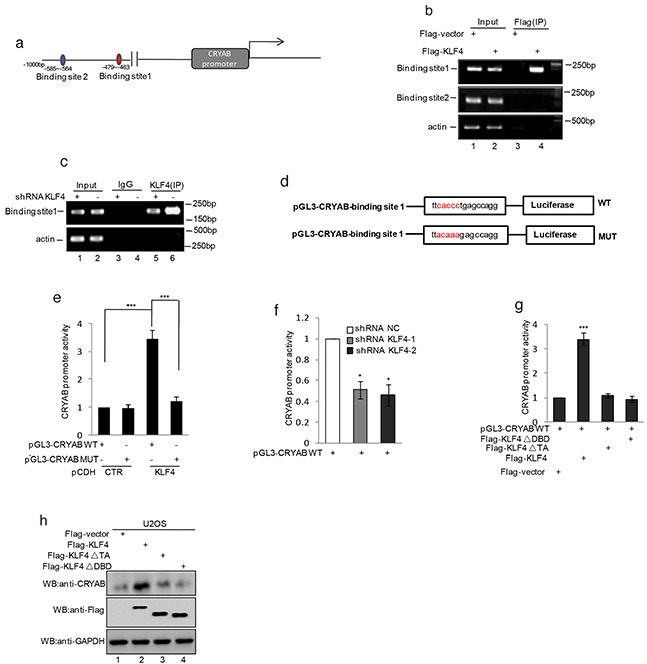
a. Schematic illustration of the putative KLF4-binding region located at 585-564 and 479-463 bp upstream of the CRYAB translational start site. b. ChIP analysis showed binding of KLF4 to the putative binding sites. Input and immunoprecipitate from MG63 cells with or without overexpressing KLF4 were amplified by PCR with primer pairs complementary to the CRYAB promoter. c. ChIP analysis showed binding of KLF4 to the putative binding sites. Input and immunoprecipitate from MG63 cells with or without knockdown KLF4 were amplified by PCR with primer pairs complementary to the CRYAB promoter. d. Schematic illustration of PGL3-basic-based reporter constructs used in luciferase assays to examine the transcriptional activity of the binding site 1. The red sequences indicate the mutated nucleotide residues. e. MG63 cells with or without overexpressing KLF4 were transfected with pGL3-CRYAB WT or pGL3-CRYABMUT. 24h after transfection, transcription activity was determined with dual-luciferase assay. f. MG63 cells with or without knockdown KLF4 were transfected with pGL3-CRYAB WT. 24h after transfection, transcription activity was determined with dual-luciferase assay. g–h. U2OS cells were transfected with pGL3-Siat7A WT as well as flag-KLF4, flag- KLF4▵TA (deletion of the transcription activity domain), or flag- KLF4▵DBD (deletion of the DNA binding domain). 24 h after transfection, transcription activity was determined with dual-luciferase assay (g). The expression levels of CRYAB and KLF4 were detected by western blot (h).
