Figure 2.
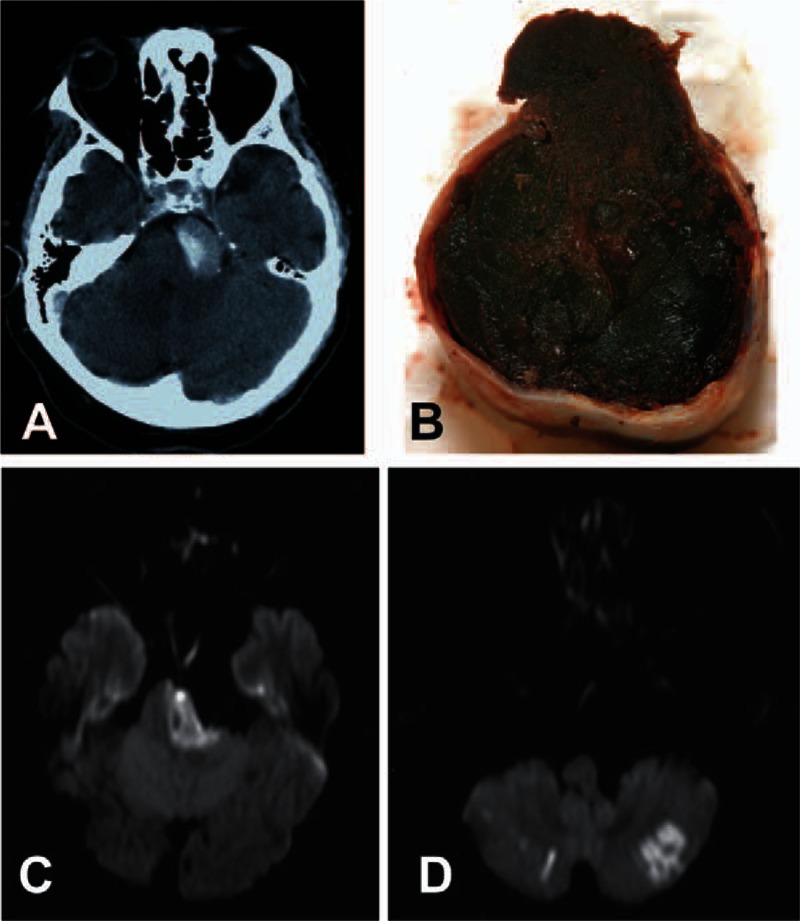
Thrombosis and stroke in dolichoectasia. (A) Axial CT angiogram revealing thrombosis within the dilated basilar trunk of a vertebrobasilar dolichoectasia (VBD). (B) Pathological examination showed multilayer acute-on-chronic thrombi. Only a small residual lumen could be detected. Rupture site (upper segment of the image) was located at the same level as the thrombus. (C) Axial diffusion-weighted MRI showing infarction of the left pons with pontine compression by the dolichoectatic basilar trunk. (D) Diffusion-weighted MRI with infarction in both cerebellar hemispheres. CT = computed tomography, MRI = magnetic resonance imaging, VBD = vertebrobasilar dolichoectasia.
