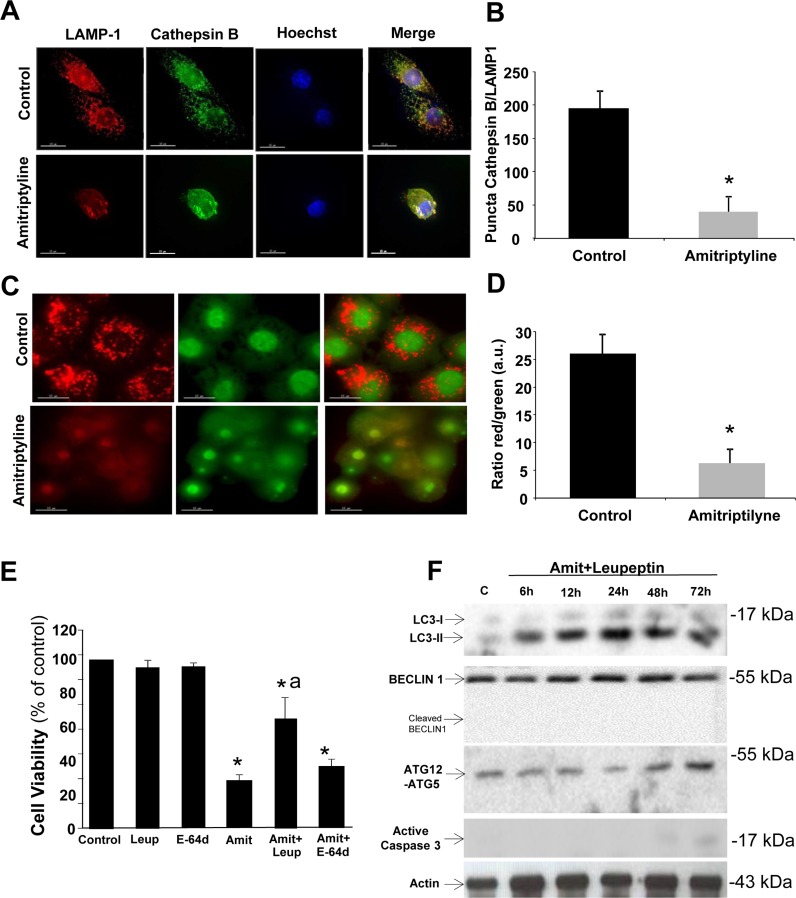
Figure 2. Lysosomal permeabilization detection by immunofluorescence.
A. HepG2 cells were treated with 50 μM Amitriptyline for 12 hours, fixed and stained for immunofluorescence detection of cathepsin B (green) and LAMP-1 (red). Note that after Amitriptyline treatment, cathepsin B diffuses throughout the cytosol. B. Quantification of colocalization puncta of cathepsin B and LAMP-1 by immunofluorescence microscopy. C. HepG2 cells were cultured for 12 h with 50μM Amitriptyline and stained for 15 min with 10 μg/ ml acridine orange. Note the loss of red staining puncta after Amitriptyline treatment. D. Quantification of the ratio between the red and green signal of acridine orange was performed by immunofluorescence microscopy using the Image J software. *p < 0.01 between control and amitriptyline-treated cells. E. Cells were seeded in six-multiwell plates, at a density of 100,000 cells/well. After 24 h culture, 50 μM Amitriptyline (Amit), were added to the culture medium in the presence or absence of 100 μM leupeptin (Leup) or 100 μM E-64d and cells were further incubated for 24h. Cells were then harvested and viability was analyzed by using the vital dye exclusion assay as described in the Materials and methods section. F. Expression levels of protein markers of autophagy (LC3, BECLIN 1 and ATG12-ATG5) and apoptosis (active caspase 3) were examined in HepG2 cells treated with 50 μM Amitriptyline (Amit) and 100 μM leupeptin for 6, 12, 24 and 48 hours by Western blotting. *p < 0.01 between control and Amitriptyline-treated cells. Actin was used as loading control. ap < 0.01 between Amitriptyline and Amitriptyline (Amit)+Leupeptin (Leup) treated cells.