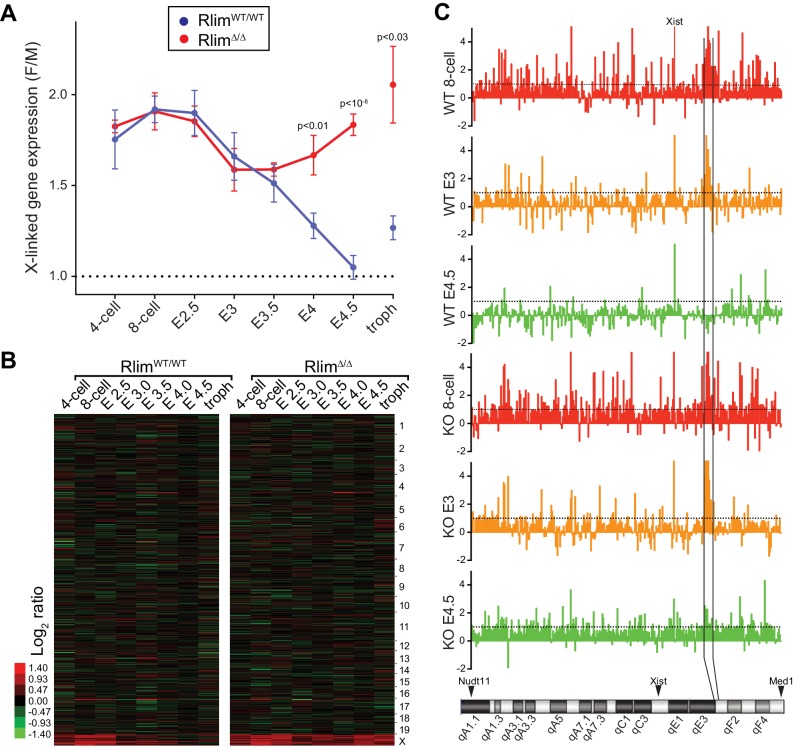
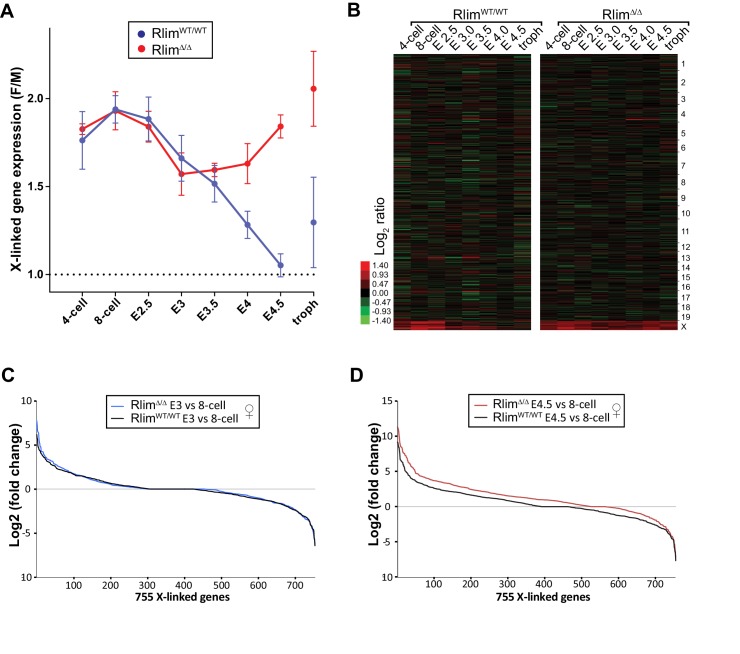
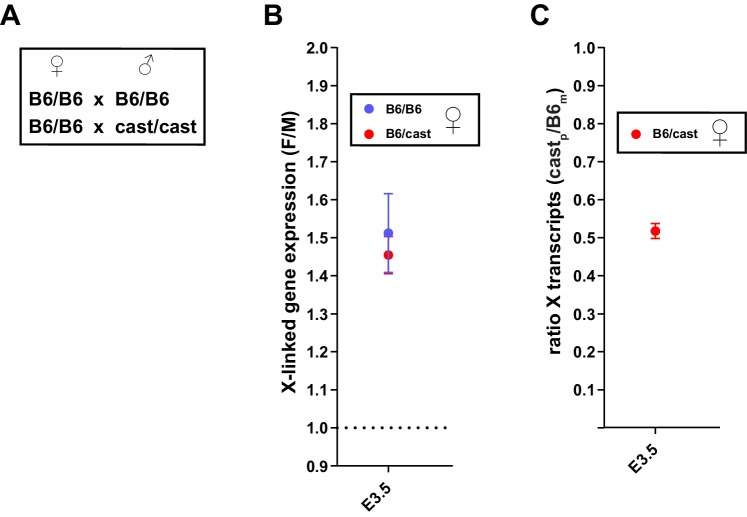
Figure 3. Rlim is required for X-silencing in females during blastocyst stages.
Female expression data collected from RlimWT/WTor RlimΔ/Δ were compared with those of male (pooled KO and WT) embryos (F/M). Embryonic stages are indicated, troph = trophoblasts. (A) Developmental profile of X-silencing during iXCI in vivo as determined by comparing mean female/male (F/M) expression ratios of X-linked transcripts (minus Xist; in Fragments per kilobase of exon per million reads mapped (FPKM)). Error bars indicate SEM. Significant p values p<0.01 are indicated (Student’s t-test). (B) Heat map representing Log2 transformed data comparing global F/M mRNA expression level ratios from chromosomes (excluding the Y) of WT and KO embryos. Chromosomes corresponding to gene expression are indicated. (C) Gene silencing during iXCI occurs within most regions on the X chromosome. Log2 F/M ratios of 351 X-linked genes at the 8-cell stage, E3 and E4.5 in WT and RlimKO are shown (values within 4.5 and -2). Horizontal dotted lines indicate Log2 values of 1. The mouse X chromosome is shown below. Arrowheads indicate locations of the most centromeric (Nudt11) and most telomeric (Med1) genes included in this analysis. Expression and location of Xist is indicated. Expression of genes within a region indicated by vertical black lines is silenced late at blastocyst stages during iXCI.