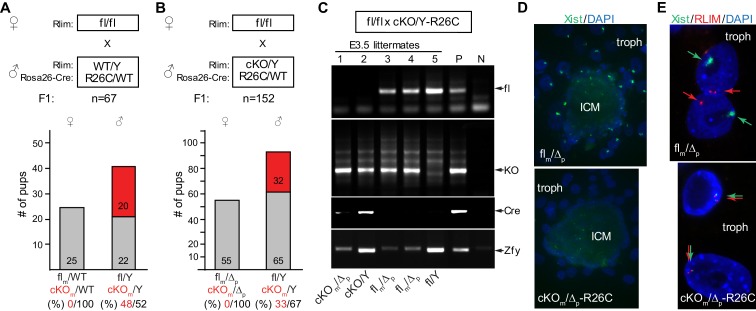
Figure 4. Embryonically expressed RLIM is required for iXCI in female mice.
The cKO of Rlim in female embryos was targeted via a paternally transmitted Rosa26-Cre (R26C) transgene. (A, B) Schematic diagram of born pups generated via indicated mating schemes. Parental genotypes with respect to Rlim and R26C are shown. For each mating, the total number (n) of F1 offspring is indicated. Numbers of female and male pups and their genotypes with respect to Rlim are indicated. The Rlim cKOm allele in pups is indicated in red. Percentages of cKOm to fl distribution in female or male pups are shown below. Note no female offspring with an R26C-induced cKO of the maternal Rlim allele. (C) Robust deletion in E3.5 embryos via a paternally transmitted R26C transgene. Parental genotypes and genotypes of embryonal littermates are indicated. A slightly slower migrating band in PCRs using primers that for the Y-linked gene Zfy is unspecific. Note that the maternally transmitted floxed allele is no longer detectable in Cre-positive embryos. Positive control (P); negative control (N). The last two bands in Zfy (P; N) originate from the same gel but have been inverted to reflect the general loading pattern. (D, E) Inhibition of Xist clouds and X-silencing in trophoblasts of E4 female blastocyst outgrowths with an R26-Cre induced deletion of maternally transmitted Rlim. RNA-FISH experiments on representative R26C-Rlim cKOm female embryos using Xist (green) and Rlim (red) probes. Note lack of Xist clouds in cKO/Δ trophoblasts (D) accompanied by X-silencing defects in most trophoblast cells as indicated by side-by-side Rlim and Xist transcription foci (E). Inner cell mass, ICM; trophoblasts, troph.