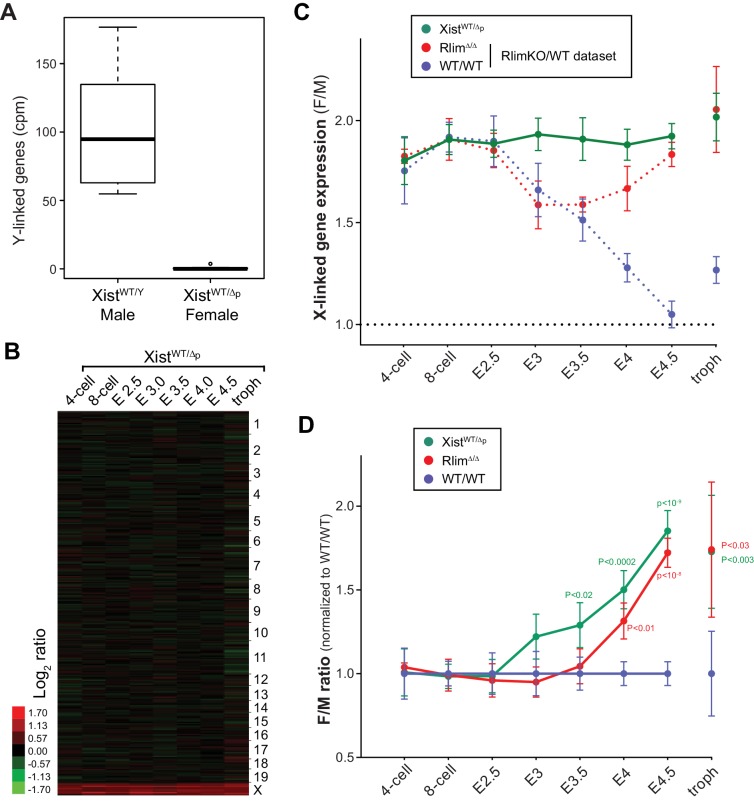
Figure 5. Xist is crucial for X dosage compensation throughout preimplantation development.
All embryos were generated by crossing WT/WT females with XistΔ/Y males. (A) Gender determination of embryos via Y-linked gene expression. As example, the distributions of reads at the 8-cell stage of Y-linked genes are shown in a box-plot. (B) Heat map representing Log2 transformed data comparing the mRNA expression level ratios from chromosomes (excluding Y) between female and male embryos during pre/peri-implantation development. Chromosomes are indicated. (C) Developmental profile of X-silencing during iXCI in XistWT/Δp females as determined by comparing F/M expression of X-linked transcripts. Data were processed as described for those obtained for the WT/RlimKO dataset which were incorporated for comparison as dotted lines (see Figure 3A). (D) Comparison of F/M values for XistWT/Δp and RlimΔ/Δ with those obtained for WT/WT (set to 1). P values of P<0.05 are indicated (paired t-test).