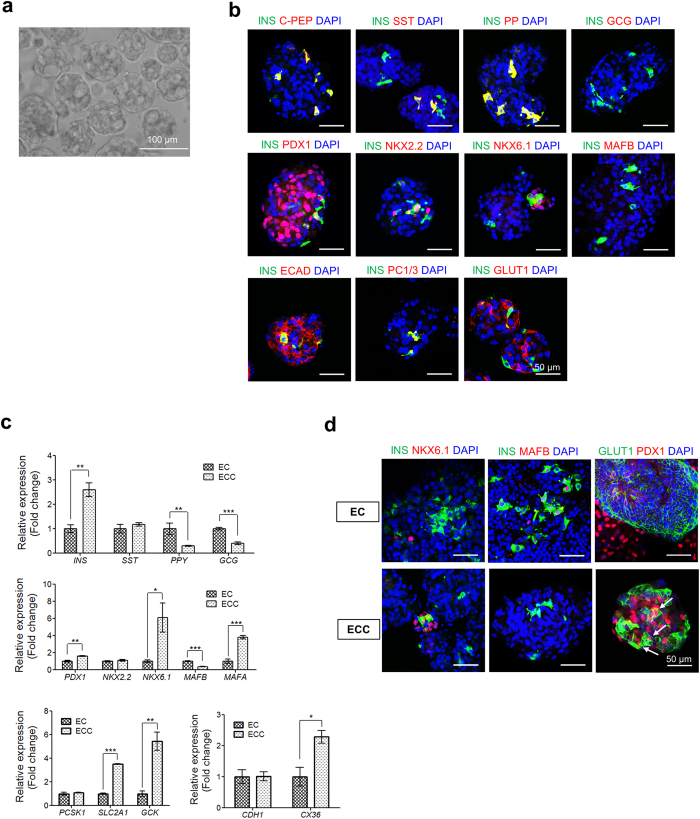
Figure 3. Efficient production of islet-like organoids derived from hESCs (hESC-derived ECCs).
(a) Representative image of hESC-derived ECCs. Scale bar, 100 μm. (b) Expression of pancreatic endocrine hormones, ß cell-associated transcriptional factors, ß cell function-related proteins in hESC-derived ECCs. Scale bar, 50 μm. (c) Comparison of transcriptional levels of endocrine hormone genes (INS, SST, PPY and GCG), ß cell-associated transcriptional factor genes (PDX1, NXX2.2, NKX6.1, MAFB, and MAFA), ß cell function-related genes (PCSK1, SLC2A1, and GCK), and ß cell gap junction-related genes (CDH1, and CX36) between hESC-derived ECs and ECCs. (d) Maturation of hESC-derived, ß cell-like cells in hESC-derived ECCs. Co-expression of INS/NKX6.1 and GLUT1/PDX1 was only detected in hESC-derived ECCs, not in hESC-derived ECs. Scale bar, 50 μm.